Basic properties of steel
In industry, ball bearing steel ШХ 15 is widely used. This is due to the special performance characteristics that allow the use of metal in the creation of bearings and blades. The name steel comes from the fact that almost all bearings are made using this material.
The characteristics of steel ШХ15 are as follows:
- Increased surface hardness. The bearings and cutting edge of the blade are subject to wear during operation. To ensure that the surface of the product does not react to mechanical stress, the hardness index increases significantly.
- Wear resistance determines that the surface does not react to friction and other impacts. Metal ШХ9 and ШХ15 are characterized by high wear resistance, so the created products can last for a long period.
- Corrosion resistance can also be called an attractive quality of the metal in question. Rust that appears on the surface reduces the service life of the product. ShKh15 steel does not belong to stainless steel. Therefore, one should not count on high resistance to high humidity and chemically aggressive environments.
- Resistance to crushing. Point exposure to high loads can lead to the formation of a dent, but the metal in question is characterized by high resistance to such effects.
- Plasticity and viscosity are also taken into account when creating various products.
- The structure lends itself perfectly to heat treatment. As a rule, hardening is carried out after giving the required shape and size. In addition to hardening, annealing and forging are performed, which can also improve the structure of the material.
- The tendency to temper brittleness determines that structural defects may appear after hardening. They can increase the fragility of the resulting product.
- Poor weldability. They were able to increase the hardness by increasing the carbon concentration. However, this chemical element significantly complicates the welding process. As a rule, to improve the quality of the weld, the workpiece is heated.
Properties of bearing steel ШХ 15
Steel grade ShKh15, which is deciphered in accordance with established GOST standards, lends itself well to various types of processing and is resistant to crushing. In addition, the surface is characterized by high hardness. The temperature of the critical points is quite high; it is taken into account when carrying out heat treatment.
Download GOST 801-78
Decoding steel
- Ш - ball bearing steel;
- X - the presence of the alloying element chromium in a volume of no more than 1.5%.
Steel ШХ15 bearing
Steel substitutes
Steel ShKh9, ShKh12, ShKh15SG.
Foreign analogues
100CrMn6 (Germany, DIN), 1.3520 (Europe, EN)
Decoding steel ШХ15
According to GOST 801-78, bearing steels are designated by the letter “Ш” at the beginning of the steel marking, after which the chromium content is indicated in tenths of a percent, i.e. for steel ШХ15 the chromium content is 1.5%
Type of delivery
- Long products, including shaped steel according to GOST 801-78, GOST 2590-88, GOST 2591-88.
- Calibrated rod GOST 7417-75.
- Polished rod and silver GOST 14955-77.
- Strip GOST 103-76.
- Wire GOST 4727-83.
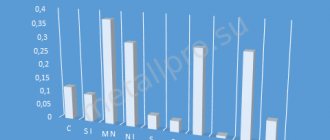
Chemical composition, % (GOST 801-78)
| C | Mn | Si | Cr | S | P | Ni | Cu |
| no more | |||||||
| 0,95-1,05 | 0,20-0,40 | 0,17-0,37 | 1,30-1,65 | 0,020 | 0,027 | 0,30 | 0,25 |
Characteristics and Application
ShKh15 steel is used for the manufacture of parts that require high hardness, wear resistance and contact strength, for example:
- balls with a diameter of up to 150 mm,
- rollers with a diameter of up to 23 mm,
- bearing rings with wall thickness up to 14 mm,
- plunger bushings,
- plungers,
- discharge valves,
- nozzle bodies,
- pusher rollers
Steel for the production of rolling bearings is supplied by:
- for hot stamping of parts - unannealed,
- for cold machining - annealed.
Application of ShKh15 steel for the manufacture of bearing parts
| Brand | GOST or TU | Profile and type of delivery | Application |
| ШХ15 | GOST 801-60 | Hot rolled and cold drawn section steel | Rings, rolling elements |
| GOST 800-55 | Pipes | Rings | |
| GOST 4727-67 | Rods | Rings, rolling elements | |
| ChMTU 1-992-70 | Rods | Rings, rolling elements |
Temperature of critical points, °C
| Ac1 | Acm | Arcm | Ar1 | Mn |
| 724 | 900 | 713 | 700 | 210 |
The influence of nitriding on the wear resistance of steel ShKh15
| steel grade | Surface hardness HV | Friction path, km | Sample wear, mg | |
| motionless | rotating | |||
| ШХ15 | 780 | 12,5 | 16 | 7,4 |
NOTE. A rotating sample made of ShKh15 steel, which in the state of quenching and low-temperature tempering has a hardness of HV780.
Hardness of ShKh15 steel after high-frequency hardening
| Hardness after quenching and tempering HRCе | Reachable depth |
| 63-67 | 8 |
Heating temperature of ShKh15 steel for high-frequency hardening
| steel grade | Pre-heat treatment | Heating temperature, °C | |||
| in the oven, in oil | with high-frequency surface heating (cooling with a water shower) and total austenitization time, s | ||||
| 10 | 3 | 1 | |||
| ШХ15 | Annealing | 830-850 | 890-930 | 920-960 | 940-980 |
| Improvement | 830-850 | 850-870 | 880-920 | 900-940 | |
Mechanical properties
| Heat treatment | Section, mm | σ0.2, MPa | σв, MPa | δ5, % | ψ% | KCU, J/cm2 | Hardness, no more |
| no less | |||||||
| Annealing at 800 °C, cooling. with a furnace up to 730 °C, then up to 650 °C at a speed of 10-20 degrees/hour in air | — | 370-410 | 590-730 | 15-25 | 35-55 | 44 | HB 179-207 |
| Quenching from 810°C in water to 200°C, then in oil; holiday at 150 °C, cool. on air | 30-60 | 1670 | 2160 | — | — | 5 | HRCе 62-65 |
Mechanical properties depending on tempering temperature
| tsp, °С | σ0.2, MPa | σв, MPa | δ5, % | ψ% | KCU, J/cm2 | Hardness | |
| HRСе | HB | ||||||
| Hardening at 840 °C in oil | |||||||
| 200 | 1960-2200 | 2160-2550 | — | — | — | 61-63 | — |
| 300 | 1670-1760 | 2300-2450 | — | — | — | 56-58 | — |
| 400 | 1270-1370 | 1810-1910 | — | — | — | 50-52 | — |
| 450 | 1180-1270 | 1620-1710 | — | — | — | 46-48 | — |
| Hardening at 860 °C in oil | |||||||
| 400 | — | 1570 | — | — | 15 | — | 480 |
| 500 | 1030 | 1278 | 8 | 34 | 20 | — | 400 |
| 550 | 900 | 1080 | 8 | 36 | 24 | — | 360 |
| 600 | 780 | 930 | 10 | 40 | 34 | — | 325 |
| 650 | 690 | 780 | 16 | 48 | 54 | — | 280 |
Mechanical properties depending on test temperature
| tsp, °С | σ0.2, MPa | σв, MPa | δ5, % | ψ% | KCU, J/cm2 |
| Heating at 1150 °C and cooling to test temperatures | |||||
| 800 | — | 130 | 35 | 43 | — |
| 900 | — | 88 | 43 | 50 | — |
| 1000 | — | 59 | 42 | 50 | — |
| 1100 | — | 39 | 40 | 50 | — |
| Sample 6 mm in diameter and 30 mm in length, deformed and annealed. Deformation speed 16 mm/min; strain rate 0.009 1/s | |||||
| 1000 | 32 | 42 | 61 | 100 | — |
| 1050 | 28 | 48 | 62 | 100 | — |
| 1100 | 20 | 29 | 72 | 100 | — |
| 1150 | 17 | 25 | 61 | 100 | — |
| 1200 | 18 | 22 | 76 | 100 | — |
| Hardening at 830 °C in oil; holiday at 150 °C, 1.5 hours | |||||
| 25 | — | 2550 | — | — | 88 |
| -25 | — | 2650 | — | — | 69 |
| -40 | — | 2600 | — | — | 64 |
Endurance limit at n=106
| Heat treatment | Hardness HB | σ-1, MPa |
| Annealing | 192 | 333 |
| Hardening from 830 °C; holiday at 150 °C, cool. In oil | 616 | 804 |
Heat resistance
| Temperature, °C | Time, h | Hardness HRCе |
| 150-160 | 1 | 63 |
Technological properties
Forging temperature, °C: beginning 1150, end 800. Sections up to 250 mm are cooled in air, sections 251-350 mm are cooled in a pit. Weldability is the welding method of CTS. Cutting machinability - Kv tv.spl = 0.90 and Kv b.st = 0.36 in the hot-rolled state at HB 202 and σw = 740 MPa. Tendency to temper brittleness - prone. Flock sensitivity is sensitive. Sandability is good.
Norms of carbide heterogeneity in bearing steel ShKh15
| Steel, delivery condition | Profile size, mm | Points of carbide heterogeneity (no more) | |
| carbide banding | carbide segregation | ||
| ШХ15, cold drawn | All sizes | 2,0 | 1,0 |
| ШХ15, hot-rolled annealed | All sizes | 3,0 | 2,0 |
| ШХ15, hot-rolled, unannealed | All sizes | 4,0 | 3,0 |
| ШХ15, wire | 5,4 >12 | 2,0 | 0,5 1,0 |
Heat treatment
The cooling rate during annealing (10-30°C/h) is set so that the decomposition of austenite is completed in the upper transformation region (up to approximately 600°C). This ensures the formation of a structure of uniformly distributed fine-grained pearlite and hardness HB (Brinell) 178-207 for ShKh15 steels.
Heating for hardening of bearing parts made of steel ШХ15 is carried out in electric resistance furnaces and salt baths. Taking into account the hardenability of steel (Fig. below), the heating temperature is set at 830-860°C for parts made of steel ШХ15 with a cross-section up to 10 mm and over 10 mm 840-870°C.
The size of the actual austenitic grain of ShKh15 steel after quenching is characterized by the curves in Fig. below. The heating time depends on the type of equipment, heating medium and section thickness.
The rings are cooled in industrial oils at a temperature of 30-60°C.
Before tempering, parts must be cooled to a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Tempering of parts made of ShKh15 steel is carried out at a temperature of 150-165°C.
The total duration of tempering is set based on exposure at a temperature of at least 2 hours for parts with a cross-section of wall thickness up to 20 mm and 3 hours for a cross-section of wall thickness of 20-50 mm. The content of retained austenite in ShKh15 steels should not exceed the values indicated in the table below.
Content of retained austenite in steel ШХ15 depending on heat treatment modes
| Initial structure of perlite | Quenching temperature, °C | Austenite content after hardening, % | Hardness HRC after quenching | Austenite content (%) after tempering at temperature, °C | |||||
| 150 | 175 | 200 | 225 | 250 | 275 | ||||
| Thin-plate | 830 | 16-18 | 64 | 18-19 | 16-17 | 10 | 3-4 | 0 | 0 |
| Fine grain | 850 | — | — | 18 | — | 10 | 5 | 1 | 0 |
| Grainy | 830 | 7-8 | 60-61 | 14 | — | 10 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
The process of nitrocarburization of bearing rings is carried out in shaft furnaces at a temperature of 860°C, the holding time is 2-4 hours, the depth of nitrocarburization is from 0.3 to 1.6 mm.
Quenching is carried out directly from the process temperature, but not lower than 820°C into oil. The HRC hardness of nitro-carburized rings made of ShKh15 steel after tempering at various temperatures is as follows: 160°C - 67-69; 200°C - 65-66; 250°C - 64-65; 300°C - 60-63; 350°C - 58-60.
The microstructure of the nitrocarburized layer consists of cryptocrystalline nitrogenous martensite with evenly distributed carbides.
After nitrocarburization, the volume of ShKh15 steel increases significantly compared to the volume of hardened steel. To compensate for this increase, changes in grinding allowances are provided. Thus, for bearing rings with a diameter of 50 to 200 mm, the allowance is reduced by 0.1-0.15 mm along the outer diameter, and the allowance along the inner diameter is also increased by 0.1-0.15 mm. For rings with a diameter of less than 50 mm and balls, the allowance does not change.
Density ρп kg/cm3 at test temperature, °С
| Steel | 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 |
| ШХ15 | 7812 | 7790 | 7750 | 7720 | 7680 | 7640 |
Linear expansion coefficient α*106, K-1
| steel grade | α*106, K-1 at test temperature, °C | ||||
| 20-100 | 20-200 | 20-300 | 20-400 | 20-500 | |
| ШХ15 | 11,9 | 15,1 | 15,5 | 15,6 | 15,7 |
Thermal conductivity coefficient λ W/(m*K)
| Steel grade | λ W/(m*K), at test temperature, °C | |||||
| 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | |
| ШХ15 | — | — | 40 | — | 37 | 32 |
Young's modulus (normal elasticity) E, GPa
| Steel grade | At test temperature, °C |
| 20 | |
| ШХ15 | 211 |
Modulus of elasticity in torsional shear G, GPa
| steel grade | At test temperature, °C |
| 20 | |
| ШХ15 | 80 |
Electrical resistivity ρ nom*m
| steel grade | ρ nom*m, at test temperature, °C | |||
| 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | |
| ШХ15 | — | 390 | 470 | 520 |
Find out more
Structural alloy steel 20ХН3А…
Steel 09G2S - structural low-alloy...
Steel 15HSND low-alloy structural...
Structural alloy steel 38ХА…
Chemical composition and structure
The steel grade in question, ShKh15, has an unusual composition, which determines its special performance characteristics. The grade belongs to low-alloy chromium steels. This determines that the composition contains a large number of special additives, which impart strength, durability and corrosion resistance. The composition includes the following elements:
- A high concentration of carbon determines increased hardness of the structure. The carbon concentration indicator is 0.95-1%.
- Manganese is included in the composition of almost any steel. In the case under consideration, the concentration is 0.2-0.4%.
- Silicon increases the strength and other characteristics of the material. SHH 15 has an indicator in the range from 0.17-0.37%.
- In most cases, corrosion resistance is achieved by adding large amounts of chromium. ShKh 15 is characterized by low resistance to aggressive chemicals and moisture, since the composition contains only 1.35-1.65% chromium.
Microstructure of Shx15 after quenching in oil
A small amount of chromium determines that it does not form its own carbides, remains in solid solution and can be part of cementite. The structure is characterized by homogeneity with small carbides. It is this property that leads to increased wear resistance.
Characteristic
ShKh15 steel received its wide industrial distribution due to its special performance properties, which are ideal for the manufacture of blades and bearings. Characteristics of ШХ15 consists of the following parameters:
- High hardness index . Bearings and blades are subjected to high loads during use, resulting in rapid wear. To prevent this from happening, the product must have additional hardness.
- Wear resistance , that is, the surface of ShKh15 is not subject to abrasion, which allows it to maintain its original working properties for a long time.
- Poor resistance to corrosion . Due to the small content of such an important element as chromium in the chemical composition, this alloy rusts when exposed to moisture, but this process does not occur very quickly due to other alloying components.
- Resistance to high shock and external mechanical loads . This metal practically does not form dents from precise impacts.
- Plasticity and toughness in the alloy in question are at an average level due to its high hardness.
- The steel structure lends itself well to heat treatment . Quenching and annealing make it possible to improve strength at the molecular level.
- Tendency to temper brittleness, which means that there is a small chance that the metal may become more brittle after quenching due to structural defects. But strict adherence to all technologies allows you to avoid this.
- Poor weldability . The alloy achieves high hardness due to its high carbon content, an element that negatively affects weldability.
pros
Having studied in detail the characteristics of steel grade ШХ15, we can draw intermediate results. Among the advantages of this alloy, the following qualities clearly stand out:
- homogeneity of structure;
- high contact endurance;
- easy to process;
- great hardness;
- excellent wear resistance;
- thin edge when sharpening;
- resistance to crushing;
- plasticity and viscosity.
Minuses
Any steel, no matter how good it is, has drawbacks - it has not yet been possible to obtain a metal that is ideal in all respects. However, the disadvantages of the ShKh15 are not numerous, among them the following can be distinguished:
- above average fragility;
- relatively low corrosion resistance;
- Difficult sharpening of cutting tools.
There are many different grades of steel. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages. ShKh 15, in turn, is a very versatile steel, suitable for almost any type of knife. At the moment it is one of the most popular brands with low cost and is used mainly in private forging of blades.
Knife Berkut, steel ШХ15, oxidation coating.
A product made from such steel can give the desired result from the work, while significantly saving the budget due to its low cost.
Processing Features
Today, heat treatment is carried out to increase the basic qualities of the metal quite often. Among the features we note:
- ShKh15 is hardened quite often. It allows you to significantly increase the hardness of the surface layer. It is worth considering that after hardening it is quite difficult to sharpen the cutting edge. Hardened steel ShKh 15 is difficult to process by cutting. That is why hardening is carried out after giving the workpiece the required shape and size. Heat treatment modes largely depend on the temperature of critical points. It is worth considering that cooling in water leads to the formation of structural and surface deformations. Cooling in the open air is carried out only in case of large product sizes.
- Annealing of ShKh15 steel is carried out at a temperature of about 800 degrees Celsius. This treatment eliminates internal stresses that cause cracks and other defects. As a rule, annealing is carried out after hardening the product. To carry out such a process, various equipment can be used.
- The workpiece can also be forged, for which it is heated to 1150 degrees Celsius. Cooling is carried out outdoors or in a pit. When forging, the structure of the material becomes more dense and resistant to various impacts.
When considering the main qualities, the tendency to temper brittleness is taken into account, as well as the ability to carry out cutting processing. A variety of equipment can be used for heat treatment. The high melting point means that improvement is extremely rare at home.
Pros and cons of steel ШХ15 for knives
ShKh15 steel has proven itself to be excellent for creating various types of knives. It is good both in the process of manufacturing a cutting tool and in its operation.
Pros:
- Can be heat treated, which improves the shape of the product and increases its strength. — The structure of the alloy is homogeneous, and this has a positive effect on the wear resistance of the knife. — A small admixture of chromium delays the rusting process. — The increased hardness of the steel keeps the blade sharp for a long time. — You can cut both meat and fruits and vegetables. The cuts are perfectly straight.
At the same time, steel has significant disadvantages, which for many become decisive when choosing a knife.
Minuses:
— Hardening of steel leads to the appearance of temper brittleness, which reduces strength indicators. — The chromium admixture is very small, therefore, without proper care, rust will appear on the steel blade after a short time. — The high hardness of the steel makes sharpening the knife difficult. It will be impossible to do without special tools.
Still, steel has much fewer disadvantages than advantages. Therefore, a knife made of steel ШХ15 is a profitable purchase.
Areas of application
The use of ShKh15 steel is largely due to the high hardness and strength of the structure, as well as insignificant corrosion resistance and wear resistance. The alloy is used to obtain:
- Balls used in the manufacture of bearings. During the operation of bearings, this element is subjected to strong mechanical stress. Therefore, special attention is paid to their production; the product is often hardened.
- Rollers with a diameter of up to 23 mm. Roller bearings that are designed for heavy loads are also available for sale.
- Plungers.
- Discharge valves. They are also subject to significant impacts at the time of operation.
- Push rollers.
Steel ball for bearing ШХ-15
The fact that the ShKh 15 alloy is called a bearing alloy determines its use in the creation of such products. They can withstand long-term use, withstand friction and other mechanical stress, and high temperature.
Application of steel ШХ 15
This carbon chromium low alloy steel has been known to technologists for about 100 years, during which time it has proven to be an excellent material for a wide range of cutting and measuring tools. The increased wear resistance of this metal has always attracted foreign knife manufacturers, while Russian manufacturers have long used manganese alloys like U8 or 65G for these purposes. Since the beginning of the 2000s, these materials have been gradually replaced by the more versatile and inexpensive steel ShKh 15.
Popular analogues such as ШХ 6 or ШХ 9 are most often used for the production of rollers and bearing balls. In turn, rings of such products, the wall thickness of which reaches 15-20 mm, are recommended to be made from ShKh15 steel. The reason is that it is characterized by much greater wear resistance and hardness.
Knives made of steel ШХ15
ShKh15 steel is characterized by versatility in use. It is used to produce a wide variety of knives, like the ShKh16 alloy. Today the brand is considered one of the most popular, which is due to its low cost. The ShKh15 knife is characterized by the following qualities:
- The blade lasts for a long period. Good wear resistance means that the cutting edge does not need to be sharpened frequently.
- The cutting edge holds its edge for a long time.
- The surface cannot be sharpened. Therefore, after its loss, it is quite difficult to restore it.
- The cutting edge is not exposed to moisture and various chemical elements. Over a long period, no rust or oxidation appears on the surface.
- The resulting blade is not brittle, the surface is hard. That is why the scope of application of the knife is expanding significantly.
ShKh15 steel is used to create products that are used under the most severe conditions. However, the material is not universal, which is due to its relatively low corrosion resistance.
Specifications
The working properties of ShKh15 steel have already been discussed above. That information is a simple explanation that follows from the following characteristics of this alloy:
- brand: ШХ15;
- class: structural bearing steel;
- specific gravity : 7812 kg/m3
- heat treatment: annealing 800oC, oven, 15 oC/h;
- forging temperature, °C: beginning 1150, end 800. Sections up to 250 mm are cooled in air, 251-350 mm - in a pit;
- hardness : HB 10 -1 = 179 – 207 MPa (61-63 HRC);
- temperature of critical points: Ac1 = 724, Ac3(Acm) = 900, Ar3(Arcm) = 713, Ar1 = 700, Mn = 210;
- machinability by cutting: in the hot-woven state at HB 202 σв=740 MPa, K υ solid. spl=0.9 and Kυ b.st=0.36;
- weldability: welding method KTS;
- flake sensitivity: sensitive;
- tendency to temper brittleness : prone;
- grindability: good.