After we have collected water from the roof along the contour of the roof, it must be drained into the ground, and not spilled over the surface of the wall, which will already receive its share of moisture from inclined rain flows.
The bracket that holds the gutter at the place where the water drains can also support a funnel, which picks up water either at the corner cut, or at the end, or in the center of the gutter into the straight section of the drainpipe. The bends are attached with special couplings, and the pipe is attached to wall with mortise screws, screwed into dowels or other connecting structures.
Types of modern gutters, their pros and cons
There are several drainage systems:
- Disorganized. Due to the sloped roof, rainwater flows directly to the ground. A significant disadvantage is that splashes and moisture get on the walls, facades, and foundations of buildings, which accelerates their destruction. It is not recommended to install in residential buildings. Suitable for arranging a pitched roof for sheds, garages, and utility buildings.
- Internally organized. Such spillways are installed in high-rise buildings. Excellent for regions with harsh climates. The pipe system is located inside the walls, so the risk of ice freezing is minimal.
- External (external) organized. Common type of fastener. The product consists of interconnected gutters and pipes through which water flows from the roof.
The shapes are rectangular and round. They are sold ready-made, but they are easy to make yourself.
There are plastic and metal drainage systems.
Made of plastic
The most popular type in private and low-rise construction. The material is polyvinyl chloride (PVC) with special additives that make the product resistant to temperature changes and ultraviolet radiation.
Among the advantages of plastic models:
- a light weight;
- resistance to sunlight (the material does not lose its properties, does not fade);
- frost resistance;
- ease of fastening;
- affordable price;
- variety of details and colors.
The operating temperature range is -40 to +70 degrees.
Among the disadvantages:
- The damaged part cannot be repaired.
- Destroys and cracks with a strong impact or fall.
- Expands when heated.
- Not suitable for use in multi-storey buildings.
Despite the disadvantages, the installation of plastic drainpipes is in greater demand due to the simplicity and accessibility of installation.
Made of metal
Metal gutters are:
- aluminum;
- copper;
- zinc-titanium;
- steel (galvanized, with a polymer layer, multi-colored).
It costs less and lasts longer when galvanized with a protective polymer coating. Moreover, the polymer layer is present both on the outside and inside. The choice of colors is large.
Among the advantages of a metal drainage structure:
- Withstands sudden temperature changes in the range from -60 to +130 degrees.
- Does not burn.
- The elements are durable and reliable, resistant to mechanical damage.
- The metal copes well with strong winds and does not deform under heavy snow loads.
The main disadvantage is that if the polymer layer is damaged, the metal begins to corrode and deteriorate.
The choice of drainage elements is small, and therefore the scope of use remains limited. It is more difficult to attach than the plastic type. The price will be more expensive.
Installation of drainage from pitched roofs
A building that is not provided with high-quality drainage during construction will, in a very short time, acquire a rather unpresentable appearance under the influence of precipitation. And most importantly, the general condition of the structure will also be negatively affected, which is why mold and an unpleasant odor may appear in many places.
A drain is needed to prevent water from accumulating on the roof and falling on the walls and foundation
And if this problem is not approached with all seriousness, the following problems will arise that will require constant financial expenses:
- high humidity will cause weakening and gradual destruction of the foundation and base of the house;
- undiverted water will penetrate into the basement and constantly fill it;
- mold and high humidity will affect the health of residents;
- the noise from flowing water will interfere with a comfortable rest.
The drainage system is used everywhere to remove precipitation from the surface of roofs: flowing water from the roof enters a special gutter and then flows through drainpipes to the ground away from the building. The purpose of the gutter is precisely to collect water from the roof surface. The drainpipe provides water drainage to a specially designated place. But to install a drain, you will need not only a pipeline and a gutter, but also elbows, clamps, fasteners and other elements.
The drain consists of horizontal gutters and vertical pipes
Gutter system configurations: closed and open
The type of roof determines the design of the drainage system. For example, for a house in a suburban area that has an ordinary gable roof with a straight eaves, a simple system with two gutters and a small number of drainpipes is best suited.
But when the roof slopes have a complex configuration, the design of the drainage system becomes more complicated. In this case, to ensure the aesthetic appearance of the building, you have to resort to various tricks to ensure reliable drainage.
Closed drainage system
A closed drain is installed if the house has a hip roof. The gutters are of a single design located along the perimeter of the slopes and do not have any plugs. It is worth paying attention to the fact that water drainage from a hip roof occurs in all directions, so drainpipes are best placed in the corners of the house.
Calculation of drainpipes in a closed system is carried out taking into account the entire roof area with values rounded up.
The choice of gutter type depends on the shape and configuration of the roof
Open drainage system
An ordinary roof with two slopes will have its own gutter with drainpipes for each slope, which means the presence of two open systems.
Drainage pipes in open systems must be installed at the corners of the building and exactly in the center of the wall.
Drainage system for pitched roofs
The simplest drainage design has a pitched roof. Sediment will flow from it in one direction, so it will not be difficult to collect it.
A pitched roof gutter consists of a small line of gutters and a downspout
In houses with only one floor, a fairly common solution is to use a rain chain instead of pipes, which is less noticeable.
The chain as a drain has become very popular on the Japanese islands, as it is also an element of facade decoration. It is often made from copper. Alas, currently manufacturers of drainage system elements for the Russian market do not produce decorative elements for drainage chains.
But if you want to make such a system yourself, be sure to comply with the following requirements:
- The chain must be tensioned to prevent it from oscillating from side to side, for which purpose the lower end must be secured in any possible way.
- To avoid water getting on the finishing materials of the building, the chain must be installed at a distance of at least 0.5 meters from the wall.
The implementation of such an idea is quite simple, the main thing is to have the desire.
The drainage chain is an excellent decorative element of the building facade
Drainage system for gable roofs
A standard gable roof has gutters that are located at the corners of the house. This arrangement is most appropriate from both an aesthetic and a technical point of view.
The installation location of gutters is directly influenced by the roof structure.
The location of the drains must be selected based on the roof plan. The installation must ensure the aesthetics and reliability of the drain, but the priority is still reliability. The length of the drain pipes is determined taking into account the distance from the gutter to the drain point (plinth area or sewer well).
The installation location of the drain pipe is also determined by the length of the roof slopes. With a length of less than 12 meters, the pipe can be located at any point on the wall, except in cases where there is a window, balcony or bay window nearby. With a length of more than 12 meters - near the center of the cornice. The main thing is that there should be no more than 24 meters between the pipes.
On gable roofs with small slopes, drainpipes can be installed in any convenient places
Gutters on roofs of complex shapes
It is difficult to design drainage for a multi-slope roof, since each slope requires its own drainage system. It is these difficulties that will be discussed in detail.
The influence of the number of slopes on the design of the drainage system
In the case where the roof has a large number of slopes, and the drainage system is built at minimal cost, a large volume of water entering the gutter sharply reduces its flow rate due to the insufficient volume of the gutter itself. This causes a large load on the system design and leads to rapid freezing of water at subzero temperatures. Therefore, when designing a drainage system, it is imperative to take into account the increase in load associated with a large area of roof slopes.
Superstructures and hatches
The next difficulty is to ensure drainage on towers or balconies, since it is in these places that moisture is most likely to penetrate into the structure and freeze. That is why building minimalism is currently fashionable.
Ensuring drainage from the tower is a non-trivial task, since it is necessary to install a gutter in the form of a circle. It is almost impossible to make a metal gutter of the required diameter by bending a single piece of material. Such a gutter is made from small segments soldered together and painted in the color of the roof to hide the junctions of the segments.
And for a roof window and skylight, a gutter is not required. The main thing is to know the direction of water flow and the place of its accumulation. In the case of lucarnes, a gutter is installed only when it has a large area and multidirectional slopes.
It is not necessary to install a drain to drain water from the hatch
Gutter elements
Their list includes:
- Gutter Designed to collect rain and melt water from the roof.
- Gutter plug. Attaches to the ends. Directs water down the slope towards the funnel.
- Gutter connector. They are used to connect gutters to each other. Tightness is achieved through a rubber seal.
- Universal angle. Changes the direction of water flow. It needs to be fixed on the inner and outer corners of the roof.
- Pipe elbow. Often used to neatly go around building façade elements. Changes the direction of water flow through a pipe.
- Funnel. Works as a water receiver. Connects gutters to pipes. Redirects water from the catchment to the drainage system.
- Drain pipe. Designed for vertical water flow.
- Connecting coupling. Pipe fastening element. Responsible for compensating for thermal expansion.
- Drain. Drains water from the system into the soil.
- Universal clamp. Allows you to attach the pipe at the desired distance from the house.
- Metal, plastic brackets. Required for installing gutters on the roof eaves.
- Straight or side bracket extension. Used when you need to attach the gutter bracket to the rafters or roof slope.
- Adjustable angle. Suitable for right angles and up to 150 degrees.
- Clamp for fastening the pipe to the facade of the building.
- Protective grille. Prevents debris from entering the drainage structure.
- Rotating eaves eaves for wall mounting.
The number and names of elements for different types of roofs may differ and be supplemented.
Free roof drainage is not the cheapest solution
Among some developers, there is an opinion that the cheapest thing to do is to do nothing - let the water flow freely from the roof directly onto the blind area and then onto the ground.
There is no need to make a special device for collecting and draining water from the roof of the house, provided:
- Increase the overhang of the roof edge from the wall to 0.6 m.
- Carry out enhanced waterproofing of the foundation and basement walls to a height of at least 0.5 m above the surface of the blind area;
- Cover the base to the specified height with a non-moisture-resistant material with high frost resistance (for example, clinker bricks or tiles, natural stone, base siding).
- Ensure that the blind area around the house and the surface of the site have a slope of several percent away from the house.
Calculate the costs of this additional work and you will see that installing a drainage system to collect and drain water from the roof will be cheaper.
By arranging a free drain without the above measures, you risk significantly reducing the durability of the finishing of the walls of the house and the basement, and reducing the bearing capacity of the soil under the foundation due to their soaking.
In addition, unorganized water flows around the site reduce the comfort of using the territory. The blind area is often used as a pedestrian path. If there is a free drainage from the roof, such a path will become impassable during rain.
Free drainage is usually used in certain areas of the perimeter of the roof of a house and outbuildings. To collect water along the edge of the blind area, it is recommended to install a tray. The system for collecting water in a tray at the edge of the blind area is less sensitive to the effects of ice and snow, to clogging with debris, and is easier to clean than a drainage system with gutters on the roof.
Next article:
How to make a roof from corrugated sheets
Previous article:
Bituminous shingles. Installation and laying of soft roofing.
⇆
More articles on this topic
- How to properly make a chimney for a boiler in a private house
- We make paths and platforms from tiles and paving stones on the site
- Interior decoration of house walls made of aerated concrete, gas silicate
- How to connect electricity to your home
- Norms and rules for planning a private house, cottage
- Height, dimensions, waterproofing and insulation of the basement of the house
- Technology for insulating facades and exterior walls of a house with do-it-yourself mineral wool
- Liquid thermal insulation as home insulation is a hoax
Gutters for drainage structures
Depending on the throughput, different markings are produced. The marking shows the ratio of the diameter of the pipe to the gutter.
The following options are considered:
- 100/75;
- 125/90;
- 150/110.
Gutters are divided into:
- semicircular;
- rectangular;
- corner.
If the first two types are responsible for collecting water from the roof, then the corner gutter changes the direction of flow.
Fixation is carried out on the outer and inner corners of the roof.
Plastic gutters can be used to make both sharp and obtuse angles. To do this, you need to cut out a part and mount the halves at the required angle. The fasteners are cold welded.
The average gutter length is from 3 to 4 linear meters. Sold individually.
They are attached to the roof with brackets and hooks in increments of 60–90 cm, maintaining a slope of 1 cm every 3–4 meters. The fewer connections there are, the faster and cheaper the installation will be.
Methods for connecting drainage gutters to each other
There are 3 types:
- Glue. The area where the gutter is fastened with a coupling with a lock and a gasket is treated with adhesive-sealant. Recommended for use in areas that will not be exposed to direct sunlight.
- Glueless. Suitable for both metal and plastic elements. The connection is made using couplings with a durable gasket that does not require sealing.
- Soldering. Suitable for steel or copper gutters. Used by craftsmen. Not suitable for joining by beginners at home - high precision is required when processing edges.
You need to choose the connection option based on the recommendations of the manufacturer of the drainage elements. In the corners, it is recommended to use adapters with high-quality seals.
Recommendations for choosing a drainage system
In accordance with SNiP standards, water flow from 1 sq. m of roof should be taken by a transverse drainpipe of 1.5 sq. m. cm . This indicator is for central Russia. For the southern part of the country the value is 1.5 times greater.
The larger the area of the roof slope, the larger the drainage elements will need to be used.
With an area of up to 50 sq. m, it is recommended to install gutters 100 mm wide and pipes 75 mm wide. If the area is 50-100 sq.m., then gutters with a width of 125 mm and pipes from 87 to 100 mm are used. For sizes over 100 sq.m, gutters with a width of 150–200 mm and pipes with a width of 120–150 mm are taken.
Rules and nuances of the installation process
It should be noted that internal drainage will work for a long time and efficiently if it is done correctly. You can carry out the calculations correctly, use the best and highest quality materials for its construction, but even the smallest mistake during assembly or installation will lead to big problems. Therefore, you should be very particular about following fairly simple rules.
- If flat small house roof
two water intake funnels
on it .
If the area is large
, then it is necessary to calculate the required
number of water intake elements
and distribute them evenly over the entire roof plane.
The set of rules and regulations states that one funnel
should be installed
per area of 20 m²
. - Funnels
must not closer
than 1 m from the walls of the building. - The distance between adjacent
funnels
connected to the same pipe riser should not be less than 20 m. - If one material was selected for the elements of the drainage system made of metals
, then it is necessary to equip the entire drain
with a heating cable
. This is a necessary measure that will protect the entire system from deformation and rapid failure.
How to properly install internal drains
If the flat roof of the house is multi-level, then each level has its own drainage system with precise calculation of elements, both in quantity and parameters
Particular attention to those multi-level roofs in which the difference between planes is more than 4 m. And once again about the tightness of the joints
This parameter deserves special attention, because repairing the internal drainage system is much more difficult than repairing the external one.
Usually the entire surface of the roof plane is divided into sections. In this case, 150-200 m² are allocated for each riser.
The slope of the roof towards the water inlet should be 1-2°.
The cross-section of the pipes is calculated taking into account the following ratio: per 1 m² of the roof plane a riser with a cross-section of 1-1.5 cm² should be installed. This is the simplest form of calculation, but it is usually effective.
All risers must be installed in heated areas of the building, otherwise there is a high probability that they will simply freeze in winter.
The funnel is installed so as to completely ensure its sealed fit to the plane of the roof structure. Therefore, rolled material is usually laid on top of the sides of the funnel.
To reduce the noise of moving water, it is recommended to cover the pipe elements with noise-absorbing materials.
How to properly install a water inlet
As practice shows, it is the installation of funnels that causes some difficulties. The main thing here is to achieve complete tightness of the clamp. Therefore, a glass is inserted into the hole that is made on the flat roof to install the water intake device. It is this that will form the water intake and ensure sealing.
The glass itself is installed only when the lining carpet is laid on the roof. That is, a waterproofing material that is always laid under the roofing covering, even a rolled one. The sides of the glass should lie on top of the waterproofing, which will already ensure the tightness of the structure. The funnel is secured using adhesives or self-tapping screws.
Then roofing material is laid on the roof. As for forming the hole, it is usually done like this:
- lay the strip roofing material
on top
of the glass
; - then cut a hole with a sharp knife exactly along
the edges of the device
; - Next, install a cap or protective
grille
.
The video shows how to correctly install an internal drainage funnel on a flat roof:
Let us add that funnels consisting of two parts are one hundred percent justified. They easily compensate for movements of the insulation when the air temperature changes.
There is one more point that concerns the effective operation of internal drainage. This is a connection of funnels to one riser. Usually, for this purpose, outlet pipe sections are used, which are laid under the ceiling of the building, but above the ceiling. Since the drainage system is a gravity flow system, these sections must be laid at a slight inclination of 1-2°. They must be insulated with noise-absorbing materials.
And lastly
Equally important is the heating system of the internal drainage system. The most important thing is to prevent pieces of ice from getting inside the system, which will block the cross-section, leading to clogging
Therefore, it is near the water intake funnels that the heating cable is laid. There are many different layout options, one of them is in the photo below.
How to lay a heating cable near a water inlet
Rules for installing gutters
It boils down to this:
- The gutters need to be hung at a slight angle of 3 to 7 degrees, then the water will drain by gravity.
- When fastening, a bracket is placed on one side of the slope closer to the eaves of the roof, and on the other side the fixation is made lower to form a slope. A thread is pulled between these brackets and auxiliary brackets are mounted every 50 cm.
- The gutters need to be laid with an overlap so that the edge of the top is on top of the edge of the bottom tray. This will avoid leaks. For reliability, all joints are sealed with silicone sealant.
- According to the standards, hang vertical drains at a distance of 12 m from each other. If the length of the facade is from 12 to 24 m, then you will have to attach 2 risers.
- The pipes are fastened to the wall of the house using clamps with self-tapping screws through plastic dowels. The fastener pitch for low buildings is 1.8 m, for multi-story buildings it is reduced to 1.5 m. Compliance with the vertical is checked with a plumb line.
- Pipes with trays are connected with funnels. At the bottom of the riser you need to drain at 45 degrees. The distance from the drain to the ground or blind area of the house is at least 25 cm.
The correct method of connecting parts of pipes is socket, when a pipe of a smaller diameter is inserted into a larger one. The joints are sealed.
Features of organizing roof drainage
Installing a roof drain is not that difficult. Most manufacturers offer ready-made circuits with detailed installation instructions.
The main task is to first think through where the water will drain from and where, make the wiring correctly and take measurements. When drawing up a drawing, you need to take into account construction standards and recommendations that have already been tested in practice.
First you need to choose the type of system - indoor or outdoor, organized or unorganized. The type of drainage depends on the number of storeys of the building and roofing material.
It is advisable to equip houses with an internal spillway over 6 levels. These are heated buildings with roll or mastic roofing. Internal drainage is also suitable for flat roofs.
An unorganized system is justified in regions with low rainfall, but requires good waterproofing of the foundation and slopes. Hidden drainage is effective and aesthetically pleasing, but difficult to install and operate.
If there are up to 2 levels, you can get by with an unorganized system. The most acceptable and recommended option according to SNiP for buildings up to 5 levels is an external organized drainage system. It is easier to install than others and is not difficult to maintain.
Before purchasing drainage elements, a drawing of the roof perimeter is drawn up with all protrusions, turns, and angles are measured. This helps to determine the system parameters and make calculations. But the drainage design must be based on justification.
There are 3 factors that are taken into account in the calculations:
- Area and design features of the roof.
- Amount of precipitation.
- Minimum possible temperature.
The diameter and footage of pipes, the number of funnels and brackets - all this depends on the roof area. If it does not exceed 100 m2, gutters with a diameter of 7-11.5 cm are suitable, the diameter of drainpipes is 7.5-13 cm. If the roof area is more than 100 m2, gutters with a cross-section of up to 20 cm and gutters up to 16 cm are needed.
When putting the elements of a drain into a single structure, you need to take into account the recommendations for the material from a specific manufacturer.
Usually, designing and choosing the type of drain does not cause difficulties. The simplest systems are created for single-pitched and gable roofs. Traditionally, two separate gutters are equipped for gable roofs, and a continuous contour for hip roofs. In frame buildings, vertical pipes are placed along load-bearing posts.
Requirements for a drainage project:
- the slope angle for installing hanging gutters must be more than 15 degrees;
- gutters are selected with a side height of 12 cm;
- structural elements are checked for compliance with GOST 7623-75, where their technical parameters and marking features are indicated;
- drain points are installed at a distance of up to 24 m;
- the diameter of the pipes is calculated by the formula - 1.5 cm per 1 m3;
- The slope angle of the gutters is 0.2-0.3 degrees or from 2 to 5 mm per linear meter.
These parameters may vary depending on climatic conditions. The standards provide parameters for the eastern system, installed in regions with average temperatures (minimal risks of freezing) and precipitation (75 mm/h).
At the design stage, it is necessary to consider a system option for collecting and draining rainwater transported through the drainage system. Ideally, it is better to dispose of it in a storm drain, but there may be other options: discharge into a collector with subsequent release into a drainage ditch, a filter well, a filtration field, a container for collecting rainwater, etc.
The number of gutters is calculated based on the perimeter of the roof and the length of one slope. Next, the number of joints of the parts is determined and it is found out how many connecting elements are needed.
When calculating the number of pipes and curved elements, you need to start from the height, perimeter of the building, and the presence of architectural protrusions
The number of fasteners depends on the chosen material for the drainage device: for metal, the distance between fasteners is 40 cm, for plastic - 70 cm. Plugs are placed on each pipe break, funnels - on each drain.
It is impossible to calculate the exact amount of materials based only on the roof area. Two roofs that are identical around the perimeter may have different gutter parameters and costs.
Here you need to collect water from each slope, bay window, and it is advisable to install several drains. If you arrange the system according to the principle of the minimum, a strong flow will enter the pipes, which will slow down as it passes through the gutters. This will create a load on the entire structure.
Sometimes additional channels for collecting water are needed above balconies, along the perimeter of towers, and in architectural superstructures. It is difficult to prevent such places from freezing and moisture penetration.
Rounded elements are especially difficult. In this case, a radius drain is made from gutters welded together, which can be painted for aesthetics.
For lucarnes and roof windows, drains are not required. They are done only if the slopes are large and multi-directional.
Another possible problem when designing drainage for a complex roof is a large number of elements. Color helps: details are selected to match the roof or contrast with it. The design also uses the shape of the profile when it is installed as an architectural element.
The installation time of the drainage system depends on the stage of construction/installation work. During the construction of the building, it is installed before the covering is laid. During the period of repair, if it was not planned to change the roof, installation is carried out at any time, but the gutter brackets in this case are attached to the front board, and not to the rafters.
Until recently, only under-roof fasteners existed. Today you can find different types of hooks and brackets that allow you to collect drainage before and after installing the roof.
The general installation algorithm looks like this:
- The location of vertical pipes is determined taking into account the placement of doors and windows. Usually these are the corners of the building or the center of the facade (if the length of one wall is more than 18-20 m).
- Funnels are installed at the lowest point of the gutter.
- Brackets are installed. The main holders are placed 10-15 cm from the funnels, the rest - at the same distance of 40-60 cm from each other.
- The gutter is placed in the brackets taking into account the expansion of the selected material.
- The gutter connectors are mounted between the brackets maintaining a distance of 10-15 cm.
- The gutter is connected to the funnels. If the gutter consists of several parts, it is more convenient to first assemble them and then fasten them along a conventional line that continues the roof. The distance is about 1 cm from the edge of the roof.
- Corners and caps are installed. If the angle of the roof is not straight, adjustable parts are selected and cut along the turning lines. This is how bay windows are treated.
- Pipes are installed 3-8 cm from the wall of the building. Plastic or metal clamps are attached to secure the drain to the facade.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Master Flash for a chimney with your own hands
The distance from the final drain to the blind area is from 15 cm, to the ground - from 25 cm. If installed lower, there will be a risk of ice forming inside the pipes, which can lead to rupture.
There must be a distance of at least 3 cm from the wall to the pipes so that the surface does not become damp. To bypass architectural elements or change the direction of drainage, a 135-degree elbow is acceptable.
Relatively recently, adjustable brackets have appeared on sale. With their help, you can adjust the bending radius by tightening the screws
Installation of plastic drainage is carried out at temperatures of 5 degrees and above. The construction of a metal system can be carried out at any time that is safe for roofers, regardless of temperature indicators. Once installation is complete, the system is ready for use.
List of materials that are needed for independent installation of storm drainage of the site and installation of the system around the perimeter of the house:
- Trays (gutters) for installation around the foundation. Manufacturing materials – plastic, polymer concrete mixture, concrete. Plastic channels are installed in areas where there is minimal physical impact on the grates: along the edges of the lawn, in flower beds. Concrete gutters are strong and durable. This tray can withstand loads of up to 25 tons. Installed in places of high loads: in courtyards where there is constant traffic, on access roads. Protective grilles are also chosen: metal and cast iron - for areas with intense load, decorative plastic - for lawns and gardens.
- Connecting elements, spacers, bases. Auxiliary materials that the manufacturer recommends to use when assembling channels. Be sure to install spacers inside plastic trays.
- Sand catchers. Separately, products are purchased for installation in a linear system and for installation in storm water inlets.
On the walls - preparation for pipe outlet
- Storm water inlets. Preferably ready-made plastic containers are used. The outer walls are equipped with preparation for connection to the outlet. Plastic receivers are easily installed on top of each other - you can assemble a container of any height.
Containers with basket and attachments
- Geotextiles. Cloth for drainage backfill channels not equipped with gutters.
Synthetic water-permeable fabric
- Crushed stone, sand. The crushed stone fraction is medium and coarse.
- Mortar for pouring the base under gutters and water inlets.
- Drainage wells. Ready-made plastic or large-diameter corrugated pipes.
Factory PVC drainage wells
- Pipes for external sewerage with fittings.
- Construction tool. You will need rough boards for formwork in the channels, pegs and fishing line for marking, shovels, picks, and a building level.
Point water inlets are stormwater and drainage elements installed under the outlet of drains. It is necessary to plan the installation so that the flow from the drain falls exactly in the center of the grate.
The edge of the well should be flush with the decorative coating
The dimensions of the hole for installing the container are determined by the height of the receiver, adding up to 30 - 40 cm for bedding and base. There should be a gap of up to 5 cm along the perimeter on each side. Dig a hole, level the walls and bottom. Be sure to check the horizontalness of the bottom and the angle so that the container does not move during installation.
Checking horizontal level
A dense ten-centimeter layer of compacted sand is formed at the bottom. A layer of crushed stone up to 25 cm high is laid on the sand cushion. It is advisable to fill the bottom with concrete mortar. The poured base is left for several days until it hardens completely, or the container is fixed in fresh solution (if necessary, permanent fixation).
Drainage planning and schemes
To understand the installation of a drainage system step by step, it is important to consider the following points when planning:
- Calculate the roof area, both total and in the section of each slope.
- Schematically depict the future installation, indicating the places where the funnels are fixed, the diameter of the gutters and the number of required elements.
- Craftsmen recommend purchasing all products from one manufacturer to eliminate discrepancies in part sizes.
- Select the system material wisely. Although aluminum and steel pipes are more expensive, they will last longer than plastic ones.
- When making calculations, take into account the standards of technical documentation, SNiP.
An important point is the location and design of the drain. Depends on the type of roof. The gable roof is equipped with two separate gutters. In a non-standard hipped roof, the perimeter becomes a solid contour of interconnected gutters.
The number of risers is determined by the length of the front part of the house. It is generally accepted that one riser is enough for every 12 m. For a larger figure, you will need to install two risers plus a compensating funnel. The last element is used, and when there are other buildings near the building or along the perimeter of the roof, it is planned to install a closed drainage system.
It is important to correctly calculate the number of long and short brackets in the form of hooks. If the roof will only be covered with material, then long hooks are fixed to the sheathing. Short ones can also be used after laying the roof, securing them to the front board.
When choosing a location for installing risers, you need to take into account the general appearance of the building so that the pipes do not spoil the aesthetics of the building. Therefore, drains are often installed in corners.
If the building frame is unusual or siding is used to finish the facade, it will be more difficult to choose the optimal location, since vertical pipes are placed next to the load-bearing supports.
Three options for drainage systems
Sometimes the installation of storm sewer, deep or vertical drainage is impossible or undesirable for various reasons. Then rain and melt water can not be removed, but collected. To do this, a suitable container must be installed under each drainpipe. If aesthetics are important, you will either have to choose a tank with an attractive design (not just a crumpled metal barrel) or take care of the decor.
This option is only suitable for regions with relatively little rainfall. In other cases, you will have to constantly monitor the emptying of water containers. It is impossible to accurately predict what the consequences of abnormally heavy rainfall will be.
Rain drainage solves several problems at once:
- eliminates stagnation of water on a flat roof, open balconies, terraces;
- allows you to organize precipitation collection at one or several convenient points (near a well, underground drainage, and so on);
- protects wall decor and the walls themselves from excessive moisture;
- does not allow the soil around the building to become wet;
- protects the foundation of the house from waterlogging, which is especially important in areas with deep freezing of the ground.
Properly organized drainage will serve for many years, will preserve buildings, and if you want and try, it will become an element of the decor of the land plot.
January 18, 2017
Installing the correct drainage system is the main task of country house owners. The absence of drain pipes leads to the accumulation of rain and melt water on the roof. A large load can lead to drops of water falling from the roof of the house every quarter of a second. Therefore, in order to avoid such a situation and to preserve the service life of the roof, you need to properly organize the drainage system.
The system of pipes through which water accumulated on the roof of a house after rain is drained and directed into certain tanks is called a drainage system. Its design includes gutters, overflow stops, connecting elements, plugs, holders, funnels, brackets and other similar parts. The complexity of the system depends on the type of roof, the facade of the house and the environment.
Before assembling a drainage system for draining and collecting rainwater, it is necessary to analyze the features of the roof. For a pitched roof, it is enough to fix only the funnels, pipes and gutters, since the liquid does not linger on the surface. In the case of flat roofs, the installation procedure is complicated by the use of an internal drainage system. Planning a drainage system allows you to determine the approximate costs of installation and purchase of parts.
At the next stage, the material and shape of the pipes are selected. Most often, round metal gutters are used, which is explained by the presence of good technical characteristics of the part. It is customary to distinguish pipes:
- Metal, able to withstand sudden temperature fluctuations and characterized by a long service life. A wide range allows you to choose models to match the color of the roof of your house.
- Plastic, which are quite fragile elements. Therefore, in practice, steel components coated with polymer substances are used. This solution allows you to organize a reliable, durable, pleasant-looking drainage system.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with How to properly dilute tile grout
Owners of country houses also have access to gutters:
- trapezoidal, original in its own shape;
- elliptical, capable of holding large volumes of water;
- square, which are the main element for creating an interesting structure design.
We perform calculations correctly
When calculating the required amount of materials, we take into account the following points:
- The standard length of gutters is 3 m. Their footage corresponds to the length of the cornices.
- One funnel is needed for each gutter.
- The number of brackets is calculated by dividing the length of the cornice into segments of 50–60 cm (this is the step with which the fastening will be carried out). Before calculating, it is recommended to leave a margin of 5 cm from the edges of the cornice.
- If the funnel is placed near the corner of the house, then one holder (bracket) is enough; when installed in the middle of the wall, two are needed.
- Each pipe branch requires two plugs.
- You will need two upper and lower elbows to assemble the riser outlet.
- If the overhang of the roof eaves is more than 25 cm, you will have to buy two pieces of pipe to connect the elbows. When suspended up to 25 cm, the knees are simply connected to each other.
- Number of pipes for the riser. To calculate it, take the distance from the ground to the cornice minus the length of the outlet and a distance from the ground of 40 cm.
- To fasten the risers you will need two main brackets and additional ones every 1.5 m.
Calculations for houses with an attic and veranda are carried out in a similar way.
Roof mounting technology
Involves installing gutters on brackets:
- to the rafters;
- on the front board;
- to the edge of the roofing material;
- using additional brackets.
Let us examine in what cases it is advisable to use different types of installation.
To the rafters
Fixing the drainage to the rafters is carried out when the sheathing has already been covered with roofing material, but it is also allowed before laying corrugated sheets, slate and various soft flooring.
The fastening element is brackets with a long leg bent at a right angle.
When the roof is covered, you will have to tear off or unscrew the last row, if it is slate or metal tiles, in order to secure the drainage system to the last row of the sheathing, the rafters. When using soft tiles or ondulin, simply lift the last row to tighten the bracket.
This method is used if the cross-section of wooden rafters is from 180*50 mm.
When fastening, the roofing material must cover the gutters.
On the front board
The front board is mounted at the ends of the rafters. Width may vary.
Fastening is carried out with long brackets or hooks made of a guide metal profile and a bracket.
Special long planks with a groove are also produced. The plank is screwed to the board with self-tapping screws, and brackets fit into the grooves.
To the edge of the roof covering
In this way, the drainage system runs along the eaves of the roof. Used when a rigid material such as corrugated sheeting has been selected for the flooring.
To fasten the brackets (plastic or metal), you will need special clamps.
There are times when you cannot do without holes in the roof. Then it is recommended to put rubber gaskets under the metal clamps (if any). This way there will be less chance of damage to the roof.
Using an additional bracket
Installation is carried out when the roofing is completed. The risk of material damage is minimized. Also, additional brackets will be required if the main brackets for fastening the gutters are short.
Take a long bracket and simply bend it to the required length, fix it with a self-tapping screw to the wooden sheathing.
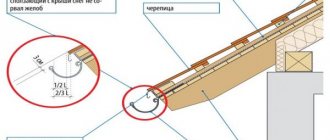
It is important to maintain the required distance from the center of the holder to the edge of the overhang. The recommended value is 30–40 mm. This will allow water from the roof to flow into the center of the gutter. Otherwise, water will overflow over the edges.
Installation features
The technology for installing a drainage system from a pitched roof is simple, but has a number of nuances that must be taken into account. One of the most important is the correct method of fastening, because this will determine how strong and reliable the system will be. The brackets must be securely screwed to the front board, sheathing or rafters at a certain pitch. Installation is carried out until the final finishing of the roof. If they are not secured correctly, the structure will begin to sag over time, causing the gutters to leak.
Plastic roof drain
An important point is the correct installation of the gutters themselves. They should be positioned so that they are partially covered by the edge of the roof - approximately 1/3. In this case, it will be possible to achieve the most efficient collection of liquid. In this case, the edge of the gutter should be located approximately a couple of centimeters lower than the slope itself - in this case, the gutter will not be damaged when snow and ice melt from the roof.
The connection of two gutters is a moment that also requires special attention. They can be fastened with glue (if they are made of plastic), couplings and seals (for plastic or metal gutters) or by soldering (the method is optimal for copper structures).
Methods for installing fasteners for laying gutters
On a note! PVC products may change slightly in size due to temperature changes, so it is recommended to connect them so that they retain some mobility. Otherwise they may become deformed.
The drain pipe itself, located vertically, should be located as close as possible to the wall of the house and secured with clamps. This will increase its resistance to wind. Individual sections of pipes, as well as pipes with funnels, are also connected using special connectors.
By the way, as for clamps for drain pipes, in the upper part, near the roof, the pipe is fixed with a rigid clamp, and in the middle or lower with a loose clamp. The distance between them should be approximately 2-2.5 m.
The runoff can be discharged directly into an underground stormwater system through a storm well, if one is available. You can also consider other options for recycling rainwater.
In what cases is drain pipe heating used?
Often during a long winter, a lot of snow gets inside the drain and ice freezes. A plug is formed, due to which the thawed water cannot flow down the pipe by gravity, so it overflows over the edges and, upon freezing, turns into icicles. There is not only a risk of damage and deformation of drainage elements, but also a danger to the lives of people nearby.
In order to prevent icing and prevent such a situation, a cable is laid inside the drain that will heat the system.
When powered by electricity, the cable generates heat. Fastening is carried out after the installation of the drain. Placed inside gutters and risers in a longitudinal position. Fixation - special clips made of plastic or metal.
A thermostat with built-in humidity temperature sensors and a power supply are supplied along with the cable. Using a thermostat, you can control the heating temperature of the cable taking into account weather conditions: reduce it when it’s warm outside and increase it when it’s very cold.
To improve the effect, the cable is also laid on the roof overhang. They do this with a snake, fixing it with clamps to the flooring material.
Advice from professionals
If you are installing an internal drain for the first time, pay attention to your specialists
- Installation starts from the bottom, gradually you need to go up.
- All channels and shafts inside the building intended for water supply must be covered with panels after its installation. This will help maintain the temperature.
- When choosing a water inlet, keep in mind that it must match the roofing material of the roof.
- The places where the funnels are installed should be slightly lower than the rest of the surface. a slight slope can be made on purpose.
- Metal pipes in the internal system must be equipped with electric heating, otherwise in winter they will freeze and may burst.
The design of the internal drainage system is more complex than the external one
It is important to pay attention to the accuracy of calculations, and during installation - to the tightness of connections
Common installation mistakes
In the absence of experience, the following mistakes are most often made:
- Failure to comply with the slope of the gutters. The recommended rate is from 3 to 5 mm per 1 linear meter. If the indicator is higher, water simply will not get there; if it is lower, areas of stagnant water and debris will form, and unscheduled drainage cleaning will have to be carried out. To correct such a defect, you have to break part of the roof.
- Saving on the number of brackets. The consequence is that an overly flexible structure becomes less resistant to wind loads, with a high risk of damage and breakage. For drainage from plastic, fasteners are carried out in increments of 50 cm, from iron and other metal - every 60 cm.
- The couplings are not connected correctly. The consequence is that leaks occur in such areas. Do not neglect the use of rubber seals and you need to seal the joints with sealant. It is recommended to double fasten the brackets (on both sides).
Craftsmen do not recommend purchasing materials for drainage from different manufacturers, since the installation process may reveal inconsistencies between elements and lack of tightness of the structure.
Step-by-step instructions for installing a drain with your own hands
Let's look at the self-fixation of the plastic system step by step.
Necessary tools and equipment
To work you will need the following set:
- metal scissors;
- screwdriver;
- hacksaw for metal or wood;
- hammer drill (to attach clamps to the wall);
- level;
- hand or electric drill;
- screwdriver;
- tape measure, pencil;
- rubber hammer;
- scaffolding;
- marker, cord (for marks);
- miter box - a tool for perpendicular cutting.
If the work is carried out with galvanization, then you will also need pliers.
Installation procedure
The recommendations are:
- We mark the places where the outer brackets are attached to the cornice. Moreover, the edge of the roof should be at a distance of up to 15 cm from the bracket.
- Now we mark where the funnels will be installed. According to the standards, one funnel goes to 50 square meters. m of roof or one funnel per slope. Place it near the edge or in the middle. We mount the bracket on the other side of the cornice. We screw the funnel to the front board or to the holder extensions (when there is no front board).
- We stretch the rope at the required slope between the funnel and the outer holder. We check compliance with the slope. We place brackets every 15 cm on both sides of the funnel.
- We fix the brackets along the remaining length of the cornice every 50 cm.
- We insert the gutters into the funnel until they snap completely into place.
- Now we insert the gutters inside with the bracket until it snaps into place.
- If the roof design requires it, we place a connector between the two gutters.
- When the funnel is attached to the edge of the cornice, in order to close it with a plug, you will have to connect these two elements with a piece of gutter. We make a section with a protrusion beyond the edge of the roof by 5–10 cm.
- Place the plug on the gutter until it clicks.
- To connect the gutters at an angle, we take a special universal angle. If the rotation is not performed at a right angle, it is better to take an adjustable angle. We seal the joints with sealant.
- Cover the top of the gutters with a protective grille.
- If there is a cornice overhang, then we connect the funnel with the pipe with two elbows and a piece of pipe of the required length. We attach a clamp to the lower knee.
- If there is no such extension, we connect the funnel with the pipe directly to each other or with a coupling.
- We connect the pipes to each other using a coupling with a gasket.
- We attach the pipes to the house with clamps every 1.5 m. To do this, screw a dowel into the facade, screw on the clamp, and tighten the clamp on the pipe.
- At a distance of 20 cm from the ground, we attach the drain to the pipe.
- On a flat roof, when the slope is adjacent to the wall, we install a rotary ebb.
At this point the work can be considered completed.
How to install vertical drainage systems
The peculiarity is that vertical drainage systems for connecting to a funnel often have several angles. Their number depends on the shape of the building.
The installation sequence is as follows:
- The distance from the wall to the funnel and the length of the coupling are determined. Two angles are selected. The lack of distance is compensated by a piece of straight pipe.
- The upper elbow must be made non-separable, that is, glued to the funnel, the others are inserted without glue.
- Markings are carried out for clamps. This is where a level comes in handy. Adhering to the vertical, points for each clamp are marked.
- Holes for dowels are drilled at the marked points. The clamps are fixed. When a brick wall has a layer of thermal insulation made of polystyrene foam, polystyrene foam or a sandwich panel finish, the length of the dowel should be enough to go deep into the wall at least 3 cm.
- The pipe is inserted. Fixed with a clamp. There are two clamps per 3 m of pipe.
- An elbow is glued to the pipe, through which water will flow onto the paving stones into a drip tray or any container. Summer residents often use the accumulated water for household purposes.
Experts advise working with plastic parts without excessive force, because no matter how durable PVC is, any impact can cause a crack to form.
Proper installation of drainage will protect the roofing and building façade from excess moisture and extend their service life. It’s quite possible to do the work yourself. Otherwise, you can order turnkey installation from specialists.
Materials: what you will need to install a storm drainage network
Storm drainage is a surface system that does not require extensive excavation work or digging deep trenches, so you can do a simple installation yourself. Before starting work, the places where lines and drainage points must be constructed are determined, and the drainage trajectory is planned. It is possible to detect all places where natural outflow is insufficient during heavy rainfall and after the snow begins to melt.
To make preliminary calculations of the amount of materials needed, it is worth drawing a diagram of the channels on the site plan.
Storm drainage installation plan
In fact, there are many more ways to arrange water drainage from a house, but some of them are intended only for large buildings and structures - apartment buildings, industrial complexes, underground passages and others. Reservoir drainage refers specifically to such systems.
The following three options are used in cases where it is necessary to organize rain drainage for private houses, cottages and other buildings, including relatively small ones.
The operating principle is almost the same as that of a city stormwater system. Its installation requires relatively small amounts of excavation work. Then it is necessary to place special rain trays in the trenches to drain the water, which are covered with gratings. This requires certain costs. But such a drainage system looks very aesthetically pleasing.
The number of drainage trenches, the size of the trays and the water collection point are calculated taking into account the expected amount of precipitation in the area.
Deep drainage
The most famous way to equip a drainage system. The implementation of this method requires more serious and voluminous excavation work than in the previous case.
The ditch for draining water should have a depth of about 0.8 m. The “filler” is a drainage pipe with perforation, which is surrounded by a layer of crushed stone and geotextile.
With this system, one or more wells are placed near the building, each with a submersible drainage pump. The technology ensures optimal pumping of water. Vertical drainage is quite complicated to design; special knowledge will be required.
The fight against high is carried out using closed underground drainage. This is a very painstaking job, but once you do it, you will insure yourself against most problems in the future. To do this, along the perimeter of the house, 2-3 meters from the foundation, trenches up to 1.5 m deep and 25-40 cm wide are dug so that there is a slope from the house building to a drainage well or natural reservoir, for example, to a pond, lake, river. Crushed stone and sand are poured into the bottom of dug ditches, and pipes with special holes (drainage holes), the so-called drains, are laid on this bed.
To prevent drainage pipes and holes in them from becoming clogged with silt and earth, they are wrapped with filter materials. Typically, plastic pipes of various diameters from 5 cm to 20 cm are used for drainage; pipes with a diameter of 10 cm with a filter are most often used.
Having laid the pipes, the trench is filled with crushed stone and sand, dug in with earth on top, on which a layer of turf is laid or lawn grass is sown. Water is collected through drainage pipes and flows into a drainage collector, and then into a water intake well, from where it is pumped out into the nearest ditch. done correctly, the groundwater level decreases, the land becomes more fertile.
If the groundwater level on the site is high, and the house has a basement or underground garage, then you will have to install a deep drainage system.
— Increased humidity in the basement; — Flooding of the basement; — Rapid filling of the septic tank (cesspool).
It is advisable to equip an underground drainage system for the foundation during the construction of a house. This will be much cheaper than removing moisture from a finished foundation built without taking into account the real groundwater level.
Water is discharged directly into a storm or mixed sewer system (by gravity - when the slope of the site is not {amp}lt; 5 mm per linear meter of pipe length) or is first redirected to storm water inlets or to a collector well, from where it is pumped out.
The slope can be either natural or artificial - for example, through the use of special concrete pipe-channels with an internal slope or multi-level stepped gutters.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Shed roof for a log bathhouse
Water collected by surface drainage can also be drained into the collector, and from there it will flow into a municipal storm drain or be absorbed into the soil (through a drainage field - a layer of crushed stone).
Arrangement of a simple drainage system
Drainage trench around the house (ring drainage)
The simplest way to drain water and neutralize the effects of ground moisture on the ground floor and foundation is to install a fairly wide drainage gutter around the perimeter of the building at a distance of one and a half to two meters from it. Its depth should be below the level of the foundation; its bottom is given a slope and filled with cement mortar.
A drainage ditch effectively removes moisture from the foundation of the house, but water from downspouts should not flow into it.
The purpose of this soil drainage system is to remove groundwater, rainwater, or meltwater from the foundation and prevent groundwater from rising during snow melt or heavy rainfall. It is a closed loop of perforated (perforated) pipes or gutters with the convex side up, laid at a depth of one to one and a half meters.
Unlike ring drainage, wall drainage pipes are laid above the level of the foundation base. The trench is paved with broken bricks or large crushed stone of several fractions; the drains are also covered with crushed stone and, together with it, wrapped in a filter material - for example, geotextiles or fiberglass. The filter prevents the drain holes from becoming clogged with silt, and the top of the trench is covered with gratings and covered with soil.
“Rotary wells” are installed at the corners of the building - they set the direction of the discharged water. The wells are made of PVC, their diameter is less than half a meter, and their height is from one to three meters.
The ditch with pipes should slope down the slope (and away from the building) and discharge water flows below the level of the basement floor. Such a drainage trench pulls towards itself, absorbs and removes moisture from approximately an area at a distance of 15-25 meters around itself.