During the operation of the Topas station, as well as similar systems using activated sludge, problems occur that reduce the degree of wastewater treatment. One part of the problems depends on the composition of the wastewater supplied to the station, the other depends on the design features and operating modes of the treatment plant.
Let's consider the most common situations that indicate problems in the operation of the Topas biological treatment plant associated with activated sludge.
SHARE WITH YOUR FRIENDS:
Operating principle of the Topas septic tank
Before moving directly to the topic of the publication, we will briefly talk about the operating principle of the Topas biological treatment station. The main task of the station is to purify the wastewater coming from the house and discharge clean water to the ground or into a reservoir. Cleaning occurs with the help of aerobic and anaerobic bacteria that live and multiply inside the septic tank.
The development of bacterial colonies is possible only when the drain is saturated with oxygen. Compressors (air traps) that operate from the network are responsible for this in the Topas septic tank.
Sludge swelling
This process in sludge biomass occurs when filamentous bacteria begin to dominate over flocculation-forming bacteria. These species have worse adsorption and oxidative properties, which entails an increase in the sludge index and a decrease in the rate of sedimentation. All these factors interfere with the normal course of the water purification process. Reasons for the formation of filamentous bacteria:
- Change in wastewater acidity (less than 6.5).
- Low oxygen content.
- Age of silt.
- Processes of fermentation and decay of waste water.
- Low nutrient content.
If swelling of sludge is detected in your treatment system, you need to take urgent measures to eliminate this phenomenon. First you need to disinfect the water. For this purpose, the processes of chlorination, ozonation or treatment with hydrogen peroxide are used. When chlorinating, a dose of chlorine (200-600 g of chlorine per 100 kg of sludge per day) is administered to the place with the highest concentration and with additional mixing (often an aeration tank).
Then the biogenic environment of the wastewater is changed - nitrogen and phosphorus are artificially introduced, and the sludge mass load and aeration rate are also adjusted.
Topas septic tank installation
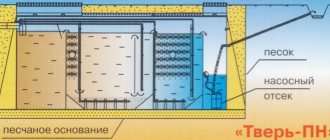
Inside the biological treatment station (BTP) Topas is divided into four chambers, and each chamber has its own function.
Fig.1. Internal structure of the Topas station
Reception chamber
serves to average runoff according to physical and chemical indicators. That is why the second name of this compartment is the homogenizer. It can be determined by the fact that drainage from the house enters there. Also in this chamber there is a coarse fraction filter - a long plastic 100 mm pipe.
Aerotank
- This is the chamber in which the main wastewater treatment occurs. In this section, thanks to the aeration element, the drain is saturated with oxygen.
In the secondary settling tank
clean water is separated from waste sludge: the sludge sinks to the bottom of the Topas septic tank, and the water is sent to exit the septic tank.
In sludge stabilizer
runoff enters when the station operates in reverse phase. It separates activated sludge from waste sludge. The waste sludge sinks to the bottom of the septic tank, and the active sludge flows into the receiving chamber.
The circulation of drainage from chamber to chamber is ensured by airlifts (mamut pumps). It happens like this: the compressor supplies compressed air to the distribution manifold, from there it enters the air tube of the desired airlift. Obeying the movement of air, water flows through the pump from one chamber to another.
Floating silt
This phenomenon occurs in clarifiers due to the reduction reactions of nitrates and nitrites contained in wastewater to nitrogen in a free gaseous state. After sufficient accumulation of released nitrogen, bubbles with adhered sludge particles move to the surface.
Floating of sludge often occurs in a layer of young biomass or at air temperatures above 25°C. To eliminate this problem, it is necessary to increase the rate of sludge recirculation, as well as speed up the process of sludge removal.
The operation of biological wastewater treatment facilities requires highly qualified treatment plant technologists and knowledge of both the basic principles of biochemical processes and the features of technical and design solutions for specific structures. In real conditions of non-stationary qualitative and quantitative characteristics of wastewater entering biological treatment, making competent operational decisions is the key to ensuring the design quality of purified water in normal operating situations and minimizing the consequences of abnormal and emergency situations. This article will examine the causes and problems of the development of processes such as swelling and foaming of activated sludge, and propose ways to solve them.
The processes of swelling and foaming of activated sludge create a serious problem during the operation of sewage treatment plants and lead to a deterioration in the quality of wastewater treatment in terms of indicators such as suspended solids and BOD, as well as to the discharge of activated sludge into water bodies. The swelling of sludge, its ascent and foaming are caused by many reasons and are associated both with the activity of various groups of microorganisms and with the conditions for the formation of activated sludge.
First, let's figure out what the processes in question are.
NOTE Swelling of activated sludge occurs due to the low ability of activated sludge to settle (the specific gravity of swollen activated sludge is slightly greater than the density of water). Foaming is the process of development of foam that floats to the surface of treatment facilities, which is separated from the main mass of activated sludge located in the volume of the structures (the specific gravity of foam is several times less than the specific gravity of water). The floating of activated sludge occurs due to the attachment of gas bubbles to the agglomerations of activated sludge flaps.
In order to make the right technological decision to eliminate these processes, it is first necessary to determine which process is currently developing at the treatment plant.
SWELLING OF ACTIVE SLUDGE
The main reason for the process of swelling of activated sludge is the development of filamentous forms of microorganisms (Fig. 1).
The processes of swelling of activated sludge from foaming can be distinguished first of all visually: if foam is observed on the surface of structures (aeration tanks, regenerators, secondary settling tanks) (Fig. 2), this indicates the development of the foaming process.
Swelling processes are characterized by the absence of foam on the surface of structures. In this case, the sedimentation properties of activated sludge sharply deteriorate.
The sedimentation properties of activated sludge are characterized by such parameters as sludge index and sedimentation rate of activated sludge. Sludge index I (cm3/g) is the volume of activated sludge containing 1 g of dry matter after 30 minutes of settling in a cylinder with a working volume of 100 cm3, and is calculated by the formula:
where Vi is the volume of activated sludge in the cylinder after 30 minutes of settling (cylinder 1-100-2 in accordance with GOST 1770-74 “Measured laboratory glassware. Cylinders, beakers, flasks, test tubes. General technical conditions”), cm3;
x is the mass concentration of activated sludge, g/cm3.
The working range of sludge index values for activated sludge from aeration tanks, in which the processes of oxidation of organic compounds occur, is 80–120 cm3/g. A sludge index value of more than 140 cm3/g indicates the presence of activated sludge swelling processes.
The main reasons for the development of certain types of filamentous microorganisms responsible for the occurrence of activated sludge swelling processes are indicated in Table. 1.
Thus, to begin with, a microbiological analysis of activated sludge should be carried out to determine the types of filamentous microorganisms that have received the greatest development. Next, using the table. 1, it is necessary to find out the possible reasons that led to the development of this type of filamentous microorganisms. Eliminating the identified causes will solve the problem of activated sludge swelling.
Figure 3 shows a microscopic picture of the different states of activated sludge (“healthy” activated sludge, swollen activated sludge and activated sludge foam).
In addition to those indicated in the table. 1 reasons for the development of various types of filamentous microorganisms, swelling of activated sludge can be caused by the following factors:
- changes in the qualitative and quantitative characteristics of incoming wastewater:
– fluctuations in flow rates and concentrations of incoming wastewater (with a ratio of maximum/minimum hourly values to the daily average of more than 1.6/0.4 for wastewater flow rates and 1.3/0.7 for BOD5 values);
– presence of toxic substances in incoming wastewater;
- incorrect design solutions for biological treatment facilities:
– discrepancy between the design air flow entering the aerobic zones of aeration tanks and the required one;
– incorrect design of secondary sedimentation tanks and the activated sludge return system, which led to the fact that the return sludge system primarily receives activated sludge settled in the central part of the sedimentation tank (the problem is more relevant to radial sedimentation tanks), and most of the sludge may be located in settling tank for more than 3–4 hours (a long period of active sludge being in oxygen-free conditions leads to its swelling);
- errors during the operation of wastewater treatment plants:
– wide range of fluctuations in the incoming load of organic compounds (+/–70%);
– high load on activated sludge for organic compounds (more than 500 mgBODtotal/gBVAI), which leads to the formation of small dispersed sludge flakes, which worsens the sedimentation properties of activated sludge.
Elimination of activated sludge swelling
In order to eliminate the swelling of activated sludge during the operation of treatment facilities, the following measures must be taken:
- if there are significant fluctuations in the incoming load of organic compounds (BODtotal, COD more than +/–70%) - increase the consumption of return activated sludge by 30–50%;
- when the concentration of dissolved oxygen in the aerobic zones of the aeration tank is less than 1.0 mg/l - make maximum use of the available capacity of the aeration system and ensure the concentration of dissolved oxygen is not lower than 1.0 mg/l;
- for pH values of the sludge mixture less than 6.0–6.5, provide for the possibility of adjusting the pH;
- at low loads on activated sludge - reduce the dose of activated sludge in aeration tanks;
- for BODtotal : N : P ratios of more than 100 : 5: 1, provide a nitrogen and phosphorus dosing system;
- when volleying toxic substances and/or petroleum products to treatment facilities, increase the air supply to the aeration tanks to ensure a dissolved oxygen concentration of about 1.5–2.0 mg/l and increase the consumption of excess activated sludge by 30–50%.
It should be noted that filamentous bacteria (such as Beggiatoa and Thiothrix) grow well at high concentrations of hydrogen sulfide and low concentrations of substrates, which gives them an advantage in conditions of low concentrations of dissolved oxygen and low loadings of organic compounds. When incoming wastewater contains fermentation products (such as volatile fatty acids and reduced sulfur compounds (sulfides and thiosulfate)), optimal conditions are created for the growth of Thiothrix bacteria. In this case, it is necessary to provide a supply of bleach to control the growth of such bacteria. When the process of swelling of activated sludge develops, chlorination of the return sludge should be carried out as an urgent (temporary) measure: a dose of chlorine in the range of 2–3 mg/l (in emergency cases - 8–10 mg/l) Cl2 per 1000 mg/l of return activated sludge .
FOAMING
When operating treatment facilities, one should distinguish between true foaming processes associated with the development of bacteria of the genus Nocardia and Microthrix, and the appearance of “white” foam at the facilities, associated with the massive entry of synthetic surfactants (surfactants) into wastewater treatment facilities (Fig. 4).
As can be seen in Fig. 4 (A), at elevated concentrations of surfactants in the wastewater entering treatment plants, a very light white foam is formed, which can be carried by the wind from the structures to the adjacent area. It is not possible to eliminate this problem using technological methods. Note that such foam is not included in the pops of activated sludge and does not have a negative effect on it.
If “white” foam appears quite rarely, then, as a rule, it disappears after 2–3 days without additional effort on the part of the technologists operating the treatment plants. If there are constant discharges of increased concentrations of surfactants, which lead to the appearance of “white” foam, it is necessary to resolve the issue of stopping such discharges by industrial subscribers and increase the dose of activated sludge to the maximum possible, which would ensure the design concentration of suspended solids at the outlet of secondary settling tanks . In addition, it is recommended to mechanically remove foam from the surface of structures.
True foaming poses a threat to the operation of biological wastewater treatment facilities - up to the complete non-sedimentation of sludge in secondary sedimentation tanks and the removal of all sludge from the structures into a treated water receiver (for example, into a river).
The development of the foaming process is associated with the slow growth of filamentous organisms (most often the genus Nocardia and M. parvicella). Under favorable conditions for the development of these microorganisms, they grow in the form of long thin threads, and under unfavorable conditions, the threads disintegrate into individual cells. Favorable conditions for the development of bacteria of this kind are a low load of organic compounds, the appearance of difficult to decompose compounds in wastewater and a low concentration of dissolved oxygen. The resulting bacterial filaments have a hydrophobic surface, which leads to their floating together with activated sludge particles. In addition, these microorganisms can release surfactants, which also contribute to the foaming process.
The foam caused by the development of microorganisms like Nocardia is dark brown, dense, and heavy. Initially, it is formed in non-aerated zones - return activated sludge channels, anoxic and anaerobic zones of aeration tanks, and then is carried into the aerated zones of structures, completely covering the surface of biological wastewater treatment facilities, incl. and secondary settling tanks (Fig. 5).
The foam caused by the development of microorganisms such as M. parvicella is gray or dark gray, greasy, and may become thick enough to have a crust (Fig. 6).
A comparison of microscopy of “healthy” activated sludge, foaming sludge and foam is presented in Fig. 7.
The main reasons for foaming are:
- low load on sludge in aeration tanks for organic compounds (less than 80–100 mgBODtotal/gBVAI);
- low concentration of dissolved oxygen in the aerobic zones of the aeration tank (less than 0.6–0.8 mg/l);
- a sharp change in the temperature regime of incoming wastewater (foaming processes most often develop in June and August in the northern regions of Russia, in May and September in the central regions, and in April and October in the southern regions);
- lack of nutrients in incoming wastewater (BODtot: N more than 20, and BODtot: P more than 100).
Malfunctions of the Topas septic tank as a result of installation errors
If you installed a Topas septic tank on your site, and it fails after a week or a month, then the reason for this may be improper installation. Professional installers do not allow this to happen. However, sometimes owners do not turn to official Topas dealers and installers, but to handymen or dubious seasonal crews. In this case, no one can give a guarantee of good installation and stably operating sewerage.
Malfunctions caused by installation errors:
- Groundwater enters the receiving chamber. This can happen due to a leaky insert on the cuff, as well as due to poor-quality soldering.
- Floating of the Topas septic tank. Reasons: either the sand around the station has not been spilled, or the chambers of the station are not filled with water.
- The phases are reversed. When starting up the station, it is important to connect the compressors correctly. If you make a mistake here, the station will not work correctly.
- Failure of the Topas station due to damage to the hull. The cause of damage may be the station falling during installation or uneven backfilling and filling with water.
- The supply pipe is always flooded. Most likely, the insertion is made lower than necessary, and when the drain level in the PC rises, the water closes the pipe.
If everything is in order with the installation, regular maintenance will ensure stable operation of the system. This preventive measure will not take much time and effort, but will significantly increase the service life of the Topas septic tank.
Reason #3
Remember, when landscaping your summer cottage, did you raise the ground level? Or during installation, did the workers install the Topas so that the neck is at ground level and below? It was so? The septic tank can overflow due to melt or storm water entering the body through the inspection lid.
Topas with equipped drainage
Solution
- It is necessary to lower the ground level near the treatment plant and provide drainage to remove wastewater.
- You can build up the neck of the septic tank to the required height. This procedure is quite common, but it will not be possible to carry it out on your own (without the proper experience, equipment and materials). By the way, our company performs similar work.
- reinstall the septic tank in compliance with the installation diagrams recommended by the manufacturer.
Symptoms of problems and their elimination
Unpleasant odor and poor drainage treatment
If you smell an unpleasant odor next to the Topas septic tank, it means that the degree of wastewater treatment has dropped sharply and this is a reason to be wary - something is clearly wrong with your station. An unpleasant odor is a symptom of almost all possible breakdowns. We will talk about some in more detail below, and about others briefly. The most likely reasons:
- Chlorine-containing chemicals were poured into the septic tank. Shower gels, dishwashing detergents and station powders are safe.
- The station has just begun its work after installation or conservation. In this case, you need to wait; the Topas station will enter operating mode within one to two weeks.
- The compressor has failed.
- The float switch has failed and the station is stuck in forward or reverse phase.
- One of the airlifts is clogged.
- There has been no maintenance for a long time.
How to fix:
In the first and second cases, it is enough to limit the use of household chemicals and wait. The bacterial colonies will recover over time and the odor will disappear. Or you can buy special bacteria and speed up the process.
In the third and fourth cases, it is necessary to stop using the sewer and promptly replace the failed parts.
I can't hear the compressors running
Possible reasons:
- One of the compressors is faulty;
- Float sensor is broken;
- Somewhere in the electrical system there is a broken contact;
- The machine gun was knocked out due to the station being flooded.
How to fix:
Failure of the Topas septic tank compressor is the most serious and expensive failure. The standard service life of a compressor is 5 years, and if it stops working earlier, then either moisture has entered it, or it’s time to replace the membrane.
In the first case, it is easier to buy a new compressor than to repair an old one, but replacing the membrane is not difficult and not particularly expensive.
In order to install a new membrane, you must:
— Unscrew the screw from the top of the cover and remove the filter. The filter can be washed and left to dry.
— Turn the compressor over and unscrew the four bolts located in the corners of the bottom. After this, the compressor housing can be easily removed.
— Disconnect the translucent L-shaped tubes connected to the membrane, unscrew four more bolts.
— Unscrew the nut holding the rubber membrane, pull out the membrane and replace it.
— Put the compressor back together.
The average cost of two membranes for an AirMac compressor is 1,500 rubles.
Overflow of the receiving chamber of the Topas septic tank
You can tell that it is overcrowded by visually inspecting the station. In this case, the water in the chamber will reach the edges of the walls between the sections and begin to overflow through them. Why is this happening?
- The receiving chamber of the Topas septic tank may be overfilled due to the excess volume of the salvo discharge. Then it is worth reducing the amount of waste discharged and trying to prevent this from happening again.
- The most common cause of PC overflow is clogging of the main airlift. If this happens, you should stop the operation of the station for a while, take out the coarse fraction filter and the main mamut pump and rinse them thoroughly with a Karcher.
Fig.2. Washed coarse filter
How to clear a blockage
— Open the lid of the Topas station and turn off the septic tank.
— Disconnect the air tubes from the airlift and the coarse filter. Mark the tubes in advance so as not to mix them up.
— Remove the airlift and filter from the clips and remove it from the station.
— Wash the airlift and filter with a Karcher or under a strong stream of water from a hose. Make sure water flows through the airlift without obstructions.
— Hang the airlift and filter back on the clips, connect the air tubes. Then turn on the station.
Cleaning the main airlift and the coarse fraction filter of the Topas septic tank is included in the standard maintenance procedure. The cost of the service is 5000 rubles.
3. Due to a malfunction of the float switch, the station may freeze in reverse phase. In this case, clean water does not leave the station, but new wastewater continues to flow from the house. This is how overflow occurs.
4. Compressor failure can also cause chamber flooding. Since the airlifts do not work, and the water from the PC does not flow further.
How to fix a broken float switch
The task of the float located in the receiving chamber of the Topas septic tank is to switch the station from one operating mode to another. There are two phases in total - forward and reverse.
In direct phase
the float is raised and the first compressor is running. It supplies compressed air to the main airlift, the fine bubble aeration element in the aeration tank and the circulation pump. In this way, the wastewater is pumped from the receiving chamber to the aeration tank, where it is cleaned, then enters the secondary settling tank and from there to the station exit.
Reverse phase
turns on when sewage from the house does not flow into the station for some time. The water level in the PC decreases and the float drops. In this case, the second compressor supplies compressed air to the aerator in the receiving chamber and the airlift of the aeration tank. The aerator in the PC promotes active mixing of wastewater in the compartment, and the airlift of the aeration tank pumps wastewater from the aeration tank into the sludge stabilizer. From the sludge collector, water flows by gravity back into the receiving chamber, the water level there rises and the float again switches the station to the direct phase.
As you can see, stable operation of the float switch is very important for the stable functioning of the Topas septic tank. If it malfunctions, the float must be promptly replaced.
Important! Problems with the float can also be due to debris adhering to it or a build-up of toilet paper. In this case, the free movement of the float may be impaired.
Removing the switch
Unplug the unit
, remove both compressors from the compressor unit.
Open the junction box cover
and disconnect the switch wires from the terminal block. Be sure to label the connectors so you don't mix them up when reconnecting them.
Loosen the sealed lead
and remove the cable from the box.
Then remove the white cable channel tube from the clip.
and remove the float switch from the installation.
Installing a new float switch
The switch cable passes through a special plastic tube and is fixed using a sealed cable gland. The “frog” of the switch must be located on the side of the sealed lead-in, and between it and the sealed lead-in it is necessary to provide a cable at least 30 cm long.
- To mount a float switch in a Topas septic tank, pull the switch cable into the channel and secure it.
- Pull the end of the cable into the junction box and connect the wires to the terminals as they were distributed before the repair.
- Connect the Topas station to power and check the operation of the switch. When the “frog” is raised, the first compressor (direct phase) should work, and when lowered, the second one (reverse phase) should work.
- Attach the cable duct to the clip.
Important! Once again, we draw your attention to the fact that when dismantling the float, you must remember which terminal goes into which cable. They cannot be confused.
A float switch for a Topas septic tank costs about 600-700 rubles.
Overflow of the entire station
It is important not to confuse this with overflowing the receiving chamber only. How to distinguish: everything is flooded above the partitions separating the chambers of the Topas septic tank. Moreover, if the station is forced, then the discharge pump is recessed under water, and if it is gravity-fed, the purified water intake is not visible.
If the entire station is flooded, then most likely the drainage pump has failed (provided for in forced Topas stations). Or the discharge froze (if the station is gravity-fed).
How to fix the emission problem
For forced stations:
- The pump is broken. In this case, the Topas station will overflow and the emergency lamp will light up. It is necessary to immediately stop using the sewer and replace the broken pump. The average service life of a drainage pump is 5 years. Price – 3,500 rub.
For gravity stations:
- The clean water discharge pipe froze. This happens infrequently, since the water coming out of the septic tank is warm. However, in severe frosts, as a preventative measure, you can wrap the emission with heat-insulating material. The asking price is 30 rubles.
- The filter well was flooded. If you have a filter well after the station as a post-treatment facility, then its flooding will cause the entire sewer system to fail. There may be two reasons for this - the well has silted up or the groundwater level has risen. In the first case, it is necessary to pump water out of the well and rinse the expanded clay. In the second, temporarily install a pump in the well and wait until the water level drops.
The alarm went off
Overfilling the Topas station may lead to flooding of the compressor unit, which should not be allowed. An alarm will help you respond to a malfunction in a timely manner. It consists of a lantern, which is located on the station cover, and a float. When the water level in the Topas septic tank rises to a critical level, the float reacts to this and the lantern lights up. If this happens, the user must immediately stop operating the sewer and call a service technician.
Fig.3. Alarm operation diagram
Important! The standard kit of the Topas septic tank does not include an alarm system. However, it provides its customers with an alarm system and its installation as a gift.
Reason #5. The most common.
Wastewater from the receiving chamber cannot pass to the next compartment (aeration tank) and, as a result, Topas overflow occurs. This occurs due to the fact that the main mamut pump (airlift) of the receiving compartment is clogged.
Mamut pump (airlift) in operation
This malfunction is associated with untimely maintenance of the septic tank, or with increased contamination of the receiving chamber with non-degradable waste (vegetable and fruit skins, hygiene products, polyethylene, etc.). Below is a diagram of how the mamut pump works.
Solution You need to check the operation of the airlift by raising the cycle switching float located inside the receiving chamber. If liquid begins to flow from the pump tube, then there is no blockage and we need to investigate further. If the liquid does not flow (and the compressor is working), then it is necessary to remove the pump from the receiving compartment, thoroughly clean it, and install it in place, remembering which tubes are connected to which nozzle.
It is advisable to begin any fault diagnosis and repair with maintenance. This simple procedure eliminates 90% of all problems associated with the operation of a septic tank. We have already written before how to do Topas maintenance with your own hands.
How to avoid malfunctions
Proper operation of the device and timely maintenance will help you avoid serious breakdowns of the Topas septic tank. Of course, force majeure cannot be ruled out, but you can protect your station from the most common malfunctions. What does that require:
- Be careful what chemicals you use. There is a wide range of biodegradable and safe laundry, dishwashing and floor cleaning products on the market. The light did not converge on “Fairy”.
- Do not allow non-degradable waste (candy wrappers, condoms, pads, hair) to get into the septic tank.
- Maintain the station regularly.
- Make sure that the station is always connected to the network. If the power is turned off, do not use the sewer.
- Do not exceed the permissible salvo release.
- Install an alarm. It will notify you in a timely manner about a malfunction of the Topas septic tank and help you avoid serious problems.
- Check the operation of the station from time to time by opening the cover.
- Trust the installation, maintenance and repair of your septic tank only to professionals. For example, !
sells, installs and services Topas septic tanks in Moscow and Moscow Region, St. Petersburg and Leningrad Region, as well as in Pskov, Yekaterinburg and Veliky Novgorod.
Reason #4
The sewer pipeline is subject to various forces, especially if it is laid deep enough underground. In our practice, there have been cases when groundwater enters the sewer line through pipe connections. Or through places where pipes are damaged. Thus, the waters flow freely into Topas, successfully overflowing it. This happens when, during installation, the connection of the sewer line to the septic tank is performed poorly. Then groundwater leaks through the weld.
Connecting the sewerage system to the septic tank
Solution Eliminate the problem in the house: check all plumbing for leaks. Make sure no occupants are using water. Pump out the receiving compartment to a level so that the socket of the inlet sewer pipe is visible. Wait a little so that all the liquid from the line drains into the septic tank. Now observe that no liquid should flow from the pipe or the seam around it into the septic tank. If it leaks, you need to dig up the line and look for the cause of the leak. We recommend that you start digging from Topas to the house in order to immediately eliminate leakage through the weld.
In all of the above cases, do not forget about the bathhouse, garage, and other buildings on the site from where water can come.
We have described external sources of septic tank overflow problems. Now let's look at internal faults of Topas.
Septic tank maintenance Topas
| Frequency of measures | Procedure |
| Once every 4-6 months (with regular use) or once a year (with periodic use) | — Excess sludge must be removed from the sludge stabilizer. — Clean the airlifts and the coarse filter. — Clean the injectors. — Remove sludge from the walls of the septic tank chambers. — Clean the compressor air filters. |
| Once a year | — Swap compressors with reconnection to power supply. — Cleaning the receiving chamber and aeration tank from sediment. |
| Once every 2 years | — Replacement of compressor membranes (for Topas 15-150). |
| Once every 3 years | — Replacement of compressor membranes (for Topas 4-12). |
| Once every 10 years | — Replacement of aeration elements. |
The user can carry out most of the work independently. It is better to entrust the replacement of aeration elements to a professional.
Important! If you don’t want to bother with servicing the Topas station, trust us to do it. When concluding a contract for regular service, a 10% discount is given.
There is a smell from TOPAS, what should I do?
When the septic tank operates properly, no unpleasant odors arise. But if they occur, then the reason is one thing: an insufficient number of processing bacteria in the septic tank. This means insufficient wastewater recycling.
What can reduce the number of bacteria? First of all, due to the ingress of chlorine, petroleum products, and aggressive surfactants into drains, which cause the death of microorganisms. The second reason is the colonization of drains by yeasts that do not get along with bacteria.
What to do if there is a smell from TOPAS? It is necessary to completely pump out the sludge from the septic tank, thoroughly clean all chambers, and disinfect it. If necessary, bacteria are updated - drugs such as Biosept, Doctor Robik, Septic Shock or others recommended by the manufacturer are used.