Modern manufacturers offer many types of shut-off valves. Products differ in purpose, principle of operation, and dimensions. It is used in the organization of oil pipelines, water supply and drainage networks.
In this article we will talk about the types of shut-off valves, their purpose and design. The information will be useful to home craftsmen, novice designers and installers. Readers will learn what belongs to shut-off valves and learn how to select suitable products.
The material contains information about locking, regulating and safety mechanisms. The article presents a classification of devices and contains recommendations for their acceptance and operation.
Valves
A common type of shut-off valve. The valves are easy to use and have a simple design. They regulate the intensity of the work flow and completely shut off the main line.
The device includes:
- frame;
- stock;
- flywheel;
- disk;
- seals;
- fasteners.
The design allows the device to be installed in heated and unheated rooms. The shut-off module is attached using flanges, and the tightness of the connections is checked visually.
Product advantages:
- low hydraulic resistance;
- moderate dimensions;
- low maintenance costs.
The valve is adjusted using rotational movements, which eliminates rapid changes in throughput.
Valves
Shut-off valves, the type and purpose of which are similar to the parameters of a valve. The main difference is the use of a spool instead of a rotary disk.
The fittings consist of the following components:
- frame;
- stock;
- spool;
- flywheel;
- sealing elements;
- connecting bolts.
The valves have a manual or electric drive. With their help, highways are laid that transport household and technical liquids. When selecting devices, the type of media, pipeline diameter, and specific external influences are taken into account.
Classification of pipeline fittings
The classification of such special structures is related to their functional purpose.
- According to the method of sealing or sealing, the fittings can be membrane, where the sealant is a membrane, bellows (the sealant is a metal shell made of stainless steel), hose (the sealant is a hose), stuffing box (the sealant is a gland seal).
- There are several types of control of such a design: remote, in which control occurs thanks to automatic actuation devices) and manual or using an electric, pneumatic, hydraulic or electromagnetic drive.
- The reinforced structure is connected to the pipeline thanks to such parts as a coupling, flange, fitting and a pipe with a collar. This is where the names of the connections come from: coupling, flange, pin and fitting. Welding is also used to connect the reinforced structure and pipe.
- Not every type of product can withstand a pressure of 200 MPa and a temperature of 800 degrees. Therefore, all types of the main part of the pipeline are divided into equipment that can maintain vacuum, withstand absolute pressure (up to 0.2 MPa), low (up to 1.5 MPa), medium (up to 15 MPa), high (up to 90 MPa), and ultra-high pressure (over 90 MPa).
- According to the temperature parameter, heat-resistant equipment is distinguished, the temperature of which is more than 700 degrees, cryogenic (below 160 degrees), low (from -10 to -50 degrees), medium (from -50 to 300 degrees) and high (from 300 to 700 degrees) fittings. ) temperatures.
- By area of application, reinforced structures are distinguished: general industrial (economy) and special purpose (for high pressure, high and low temperatures, toxic environments), specialized (to order), marine (for the construction of various sea vessels) and plumbing (various household appliances) .
The types and classification of pipeline fittings are closely related to each other, since they perform functions related to the efficient and safe operation of the pipeline.
Valves
The use of check valves prevents the working flow from moving in the wrong direction. Pipeline fittings of this type protect pumping, filtration and metering equipment. It ensures correct operation of the containers and minimizes the loss of working media in the event of a leak.
Advantages of pipeline valves:
- possibility of operation at high pressure;
- simple maintenance;
- preventing the backflow of gases and liquids;
- moderate dimensions;
- quick and easy installation;
- variability of execution.
Products can be classified as safety elements. It is an integral part of industrial and utility pipelines.
Types of pipeline fittings
In total, there are 7 types of such products according to their intended purpose: shut-off, regulating, safety, protective, phase separating, mixing and distribution, control.
- Shut-off – represented by gate valves, taps, dampers and valves. Ensures complete cessation of the movement of working fluid in pipes for its release into the environment, or for entering control and measuring instruments.
- Regulating - represented by valves, self-regulating valves, steam traps and special devices that regulate the required flow level. Provides the ability to change temperature, pressure, pressure and flow of a substance in a certain state of aggregation.
- Safety - represented by safety and bypass valves, as well as a diaphragm fuse. When the pressure in the vessel increases above normal, it ensures automatic opening of the valve and discharge of excess substance.
- Protective - represented by shut-off and check valves, or pneumatic valves. Provides automatic emergency shutdown of a separate section or the entire pipeline in the event of a critical change in the performance of the working material.
- Phase separation – represented by oil separators, plungers and condensate drains. Serves for automatic separation of phases of the working substance, which is in different states of aggregation, and their removal.
- Mixing and distribution - presented in the form of special mixer taps that distribute flows and valves. Provides mixing of different flows of the working substance into one, or divides one flow into several flows going in different directions.
- Control - represented by plug valves and level sensors. Serves to determine the movement and level of working material, which is in a certain state of aggregation.
Gates
The key purpose of the gate is to completely block the highway. The product includes:
- rotary handle with lock;
- cast metal body;
- disk;
- stock;
- seals.
Features of gate installation depend on the type. The device can be installed by one or two craftsmen; there is no need to use complex tools.
Equipment advantages:
- simplicity of design;
- availability of compact models intended for household use;
- possibility of installation in non-electrified areas;
- moderate weight.
Products for critical facilities are selected according to design documentation.
Symbols of shut-off valves
Special figures are used to schematically display shut-off valve products. As a rule, they consist of triangles in different positions.
They have their own designations:
- globe and angle valves;
- taps and valves;
- circuit breakers;
- valves;
- gates;
- fire and watering hydrants;
- devices with double adjustment;
- faucets;
- water meters.
Designations are regulated by current standards and are used when constructing general and profile diagrams.
Scope of application of fittings
According to the main purpose, two types of fittings are distinguished:
- Industrial;
- Special (taking into account customer requirements).
Depending on the area of application, pipeline fittings can be of several types:
- General purpose (serial production);
- For special conditions (for high-tech, chemical, highly toxic, and energy systems);
- Special (ordered by the Ministry of Defense, for nuclear power plants - has special requirements);
- Ship transport;
- Plumbing (small diameters, serial, with increased requirements for appearance).
Requirements for shut-off valves
Locking mechanisms for technical lines must meet the following requirements.
- Structural integrity. Mechanical damage is unacceptable. This applies to the body, connecting and control elements of the valves. The use of defective products will reduce the efficiency of the network and will not allow flow control.
- Tightness. Products must be equipped with high-quality seals. The presence of leaks and fogging indicates problems with the gaskets or incorrect formation of the connection.
- Smooth adjustment. The presence of jamming and jamming indicates a breakdown of the working mechanisms. Serviceable fittings ensure smooth movement of moving elements.
- Completeness. The certified product is supplemented with accompanying documents. They are requested upon acceptance and confirm product compliance with industry standards.
Shut-off valves are checked before installation. The presence of obvious and hidden defects is a reason to refuse to use the product.
Types of shut-off and control valves
Regulating equipment for pipelines differs in purpose and specific operation. There are six groups of devices.
- Industrial. Solutions for manufacturing enterprises. The equipment is highly durable and is produced in large quantities.
- For particularly dangerous areas. Reinforced devices equipped with heating, shock-resistant housings, and special seals. The products work in chemical and explosive enterprises, and are used in the Far North and mountainous regions.
- Profile. Narrowly targeted equipment, in demand in small quantities. The products are used at nuclear power plants, in laboratory and experimental workshops. There are special requirements for the quality of these products.
- Custom. Atypical products that are produced in limited quantities. The fittings are produced according to individual drawings and unique technological maps. Custom-made products differ in design, ergonomics, and functionality.
- Garden. Products for household needs. With its help, watering lines, sprinklers, and storage tanks are connected. The products are small in size and operate in networks with low pressure.
- Plumbing. Fittings used in public utilities. It is in demand when connecting apartment buildings, infrastructure facilities, and municipal buildings.
When implementing a project, various types of reinforcement can be used. Equipment is selected through calculations.
Pipeline fittings are divided into several classes.
- Constipated. Devices that open and block the channel. The simplest type of product.
- Regulatory. Equipment that corrects flow intensity by partially blocking the line. The adjustment accuracy depends on the model.
- Distribution and mixing. Solutions that distribute and combine flows. They are in demand when working with reagents and are used in production.
- Safety. Installations that prevent pressure drops, line breaks, and reverse fluid flow. The product requires minimal calibration and has a wide range of applications.
- Protective. Fittings that level out the consequences of accidents. Its presence prevents damage to pumps, filters, and accounting modules.
- Phase separation. Solutions that separate the working environment into several phases, for example liquid and gaseous.
A competent combination of fittings will allow the implementation of complex technological solutions and ensure uninterrupted functioning of the network.
Locking devices: classification and application
The main types of shut-off valves for pipelines are valves, valves, flaps, taps and valves. Gate valves are characterized by the movement of the locking element at right angles to the longitudinal axis of the pipe, while valves are characterized by parallel movement.
Valves
It is possible to use valves on shut-off products with a diameter of up to 0.3 m. They are often used in the final (dead-end) sections of the system during repairs. The locking element, often a body of rotation or part thereof, rotates around an axis located at an arbitrary angle relative to the axis of the pipe. Valves can be used not only as shut-off valves, but also as control valves.
Valves
Gate valves are short-length shut-off elements designed to operate in systems with low hydraulic resistance.
By design, they are wedge (with a composite, elastic, solid wedge) and parallel (gate). In systems with low pressure, valves of the latest type are used.
The main purpose of valves is to perform locking functions; in most cases they are not used as regulatory elements. During operation, the valves can be set to two possible positions: closed or open.
It is best to use such elements in full-bore systems, that is, in the absence of a reduction in the cross-section of pipes in the nozzles. For example, valves are ideal for use in main pipelines where the working fluid moves continuously and at high speed.
A distinctive design feature of the valve is the presence of a spindle, which, depending on the design, extends or not.
As already noted, there are two main types of valves: gate valves and wedge valves.
The design of the gate elements includes a metal wedge that, when moving, cuts foreign elements of the working environment. Gate valves are equipped with pipelines for fecal wastewater, pulp and paper production, etc.
If it is necessary to carry out periodic repairs of system elements, wedge valves are installed, consisting of a cast-iron body, inside of which a rotating spindle connected to the wedge is installed. Wedge valves are used when servicing systems for transporting gases and liquids that do not react with the pipeline material. The body and cover of such products are welded from parts cut from corrosion-resistant or carbon steel sheets.
Valves
The purpose of the valves is to open and close under certain conditions, for example, when a certain pressure level is reached or the direction of movement of the working fluid changes.
Products are divided into single- and double-saddle, and usually the second type is used in production, which simultaneously performs distribution and control functions.
Based on the direction of flow of the working medium, valves are divided into angular (the direction changes by 90°), through (the direction does not change) and straight-through (the line of movement of the medium is straightened).
To completely block the flow inside the pipes, shut-off valves are used. This fittings ensure maximum reliability and tightness of the system.
If there is a need to prevent a change in the movement of the working medium (for example, if the pump fails and the carrier channel is damaged or broken), check valves are used.
With the help of control valves, you can control the amount of liquid or gas supplied to the system by changing the size of the inlet.
Shut-off and control valves, as the name implies, perform two functions simultaneously.
Cranes
A more universal option for pipeline fittings is taps. They can be used as shut-off, control or distribution devices. The taps are suitable for any, including viscous, liquids and gases. Repairing these devices requires a lot of effort and experience.
Valves consist of a valve (or plug) of spherical, cone-shaped or cylindrical geometry, with a hole in the center, and a body. These locking elements are made from brass, bronze, cast iron and steel, and in the case of more aggressive internal conditions - from porcelain or special plastic.
Cranes are usually divided into groups depending on:
- direction of flow and number of nozzles (through, three-way, angled, multi-pass);
- the principle of shutter movement (with spin, or lifting, or with rotation, without lifting, shutter);
- control method (manual, with electric, pneumatic, hydraulic drives);
- shutter geometry (needle, cone, ball, cylindrical);
- method of ensuring tightness (stuffing or tension).
Where is the best place to buy shut-off valves?
EcoMontazh offers shut-off valves in various designs. Solutions for private and industrial use are on sale. Equipment for oil pipelines, heating networks, and drainage lines is presented.
Key benefits of cooperation with clients.
- High quality product. Only certified equipment is on sale. The products are supplied in original packaging, accompanied by quality certificates and certificates of conformity. The products undergo factory testing, which is indicated accordingly in the documents.
- Prompt delivery. The goods are sent anywhere in Russia. The company cooperates with transport companies and offers preferential conditions for wholesale customers (reduced costs, favorable cooperation schemes). Pickup of paid products from the warehouse is possible.
- Lots of related products. Along with shut-off valves, welding machines, polymer pipes, fire hydrants, etc. are sold. The range of products is periodically expanded.
Company managers will help you purchase equipment. They will talk about the features of cooperation and recommend solutions that meet the client’s requirements. Orders are accepted by phone, via e-mail or feedback form.
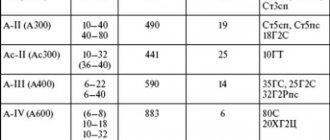
Symbol of fittings according to the TsKBA classification (table-figure)
The symbol for valves accepted in the valve industry (TsKBA classification) consists of numbers and letters. The first two digits indicate the type of fittings (see Table 1).
The letters behind the numbers indicate the material used to make the valve body (Table 2).
One or two digits after the letters are the model number; if there are three digits, the first of them indicates the type of drive (Table 3), and the next two indicate the model number.
Table 1
| Type of fittings | Symbol |
| Bleeding valve | 10 |
| Pipe valve | 11 |
| Level indicator locking device | 12 |
| Shut-off valve | 13, 14, 15 |
| Shut-off valve | 22, 24 |
| Check Valve | 16 |
| safety valve | 17 |
| Reverse shutter | 19 |
| Bypass valve | 20 |
| Pressure regulator | 18, 21 |
| Distribution valve | 23 |
| Control valve | 25, 26 |
| Mixing valve | 27 |
| Gate valve | 30, 31 |
| Butterfly valve | 32 |
| Hose valve | 33 |
| steam trap | 45 |
table 2
| Housing material | Symbol |
| Carbon steel | c |
| Alloy steel | PM |
| Corrosion-resistant (stainless) steel | nz |
| Gray cast iron | h |
| Malleable iron | CC |
| Ductile iron | HF |
| Brass, bronze | B |
| Aluminum | A |
| Monel metal | pl |
| Plastics (except vinyl plastic) | P |
| Viniplast | VP |
| Porcelain | To |
| Titanium alloy | tn |
| Glass | sk |
Table 3
| Drive unit | Symbol |
| Under remote control | |
| Mechanical with worm gear | 3 |
| Mechanical with spur gear | 4 |
| Mechanical with bevel gear | 5 |
| Pneumatic | 6 |
| Hydraulic | 7 |
| Pneumohydraulic | 6 (7) |
| Electromagnetic | 8 |
| Electric | 9 |
The last letters indicate the material of the sealing surfaces (Table 4) or the method of applying the internal coating of the housing (Table 5).
Table 4
| Sealing surface material | Symbol |
| Brass, bronze | br |
| Monel metal | pl |
| Corrosion-resistant (stainless) steel | nz |
| Nitrided steel | nt |
| Babbitt | bt |
| Stellite | st |
| Sormait | Wed |
| Leather | To |
| Ebonite | uh |
| Rubber | R |
| Plastics (except vinyl plastic) | P |
| Viniplast | VP |
| Fluoroplastic | ft |
Table 5
| Internal coating method | Symbol |
| Gumming | hmm |
| Enameling | Em |
| Leading | St. |
| Plastic lining | P |
| Nairite lining | n |
A product without inserted or welded-on rings, i.e., with sealing surfaces made directly on the body or valve, is designated “bk” (without rings).
Along with the TsKBA system, they use a code obtained by abbreviating the name of the product, for example KSh-16/15 - a ball valve with a nominal pressure of 16 kg/cm² and a nominal bore of 15 mm. Some designs are designated only by the number of the drawing according to which they are manufactured; sometimes the letter of the name of the manufacturer is entered into the product designation.
The symbol for valves intended for the oil refining and oil production industries consists of letters and numbers. Letters indicate the type of product, numbers indicate product parameters. For example: ZKL2-200-16 - cast wedge valve of the second modification with a nominal bore of 200 mm for a nominal pressure of 16 kg/cm².
In catalogs of pipeline fittings, abbreviations are usually used to designate the working medium (Table 6).