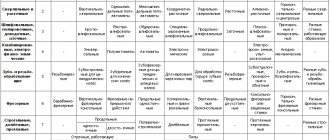
instruments vary according to:
grain size - the larger the grain, the stronger the wheel and the smaller the grain, the harder the wheel. That is, hard wheels with small grains are used for finishing operations at high speeds when processing hard materials due to increased heat resistance, and durable wheels with large grains are used for roughing and roughing operations due to greater resistance to impact loads.
form:
cup, flat (with or without grooves, as well as with relief)
material:
diamond, abrasive, CBN, etc.
by type of base:
hard - grinding wheels, heads, segments, bars; flexible - elastic wheels, abrasive belts and sandpapers; liquid - pastes, suspensions.
Grinding wheels are used when the main movement due to which the processing will be carried out is rotational. Therefore, they represent bodies of revolution of different shapes.
Flat wheels are used for external, internal and centerless grinding, for surface grinding on the periphery of the wheel and for sharpening tools.
Cylindrical and conical cup wheels are used for sharpening tools and end grinding.
Disc wheels are used for sharpening and finishing the front edges of cutters, processing the teeth of cutters and other tools.
On cylindrical grinding machines, grinding is carried out using grinding wheels.
Types of grinding processing:
- Cylindrical grinding is the processing of cylindrical surfaces, both internal and external. Such as shafts, flanges, etc.
- Flat grinding is the processing of the planes of a product, and it can be carried out both at the end and at the periphery of the wheel.
- Centerless grinding - grinding of parts such as shafts - plungers, rollers - that are not in a fixed state. The surface treated with the base is technological. A knife with a beveled edge, located between the driving and working circles, supports the part, and by adjusting its position, you can adjust the relative position of the part.
- Profile grinding - during profile grinding, special wheels are used, which with their shape determine the shape of the surface after processing. Such profile grinding operations are used in the manufacture of broaches, backing of cutters, etc.
The purpose of cylindrical grinding machines is to process the external and internal surfaces (cylindrical and conical) of the part (located in the centers or chuck). Important characteristics of such machines are: circle diameter and rotation speed, table size, center sizes. The processing is carried out with an abrasive tool - this is a cutting tool made from grains of grinding materials, linked together by a binder (binder) and separated from each other by pores.
It is carried out by summing up several movements carried out by the machine: rotation of the abrasive wheel (main movement), linear movement of the part or cutting tool along a straight path (longitudinal feed), transverse movement (plunging movement) due to which the allowance is removed from the workpiece, as well as rotation of the part (circular feed).
Grinding is used to give the workpiece the required shape, obtain the dimensions of the part specified in the drawing and the required surface roughness. Finishing and finishing processing of workpieces by grinding can ensure dimensional accuracy of 5...7th quality; shape accuracy - 6...10th degree and roughness with a height of micro-irregularities 1.2...0.1 microns. Examples of parts (bushings, shafts, etc.).
Cutting occurs due to the removal of allowance by micro grains - cutters located in a random position and at some distance from each other. Due to the high hardness of these grains, it becomes possible to process particularly hard materials at high speed. But at the same time, a high instantaneous temperature (1000-1600 ◦C) arises in the contact zone, which forms a burn on the surface of the part, causing residual stresses and microcracks, which causes a strong decrease in the durability (by 3-4) of the part.
The grinding wheel is driven by a separate motor through a V-belt drive. Circular feeding of the workpiece is carried out using another electric motor with stepless control.
The longitudinal feed movement is communicated to the lower table using a hydraulic drive; movement is controlled using devices that are switched by the table itself in its extreme positions. The grinding head is also periodically moved in the transverse direction using hydraulic mechanisms. Most machines have mechanisms for wide regulation of grinding modes and means of automating the working movements of the table and grinding headstock. It is possible to use active control devices that allow you to measure the workpiece during the grinding process, as well as devices that automatically stop the machine when the required size is reached.
When processing on cylindrical grinding machines, the workpiece is most often mounted in rigid (non-rotating) centers located on the headstock and tailstock; in this case, the circular feed is provided by a drive device connected to a rotating faceplate. It is also possible to secure workpieces in jaw chucks, and when grinding non-rigid workpieces it is additionally necessary to use steady rests.
These machines are divided into the following types: cylindrical grinding machines - center and centerless; machines for internal grinding.
Machines, regardless of their design features, have the following standard components and mechanisms: bed (base for all machine components); table (provides reciprocating movement and circular feed of the part) the table drive is usually hydraulic; headstock and tailstock; a grinding head (in most machines it feeds the tool transversely), to which the abrasive wheel is attached.
High processing speed, allowing you to grind thin-walled parts even from soft metals;
- The special technology of the grinding process reduces the likelihood of runout;
- High accuracy of obtaining ideal cylindricity of the part.
- This equipment is used to create automated lines.
Advantages of ordering in
Clients turn to us to buy a cylindrical grinding machine or other equipment for processing metal parts, because we have created favorable conditions for them. In addition, the company maintains high standards of service for both regular and new customers and strictly complies with all obligations stipulated by the contract.
The following advantages of cooperation with our company can be highlighted:
- professional assistance in selecting equipment for mechanical engineering enterprises, based on the requirements and financial capabilities of buyers;
- provision of services for installation, commissioning and commissioning of universal cylindrical grinding machines;
- convenient payment methods, sale of equipment on lease, favorable payment schemes;
- delivery to all regions of the Russian Federation and CIS countries to customer enterprises;
- provision of maintenance services for machine tools;
- a large selection of equipment for machine-building plants, repair organizations using machine tools;
- system of discounts and installments;
- models from leading manufacturers.
Cost and delivery conditions
Cylindrical grinding machine is equipment for roughing and finishing the outer surface of parts. Design features allow you to work with workpieces of various shapes: cylindrical, conical, straight. Diamond and grinding wheels are used as working tools.
The low grain size of the processing tool ensures a slight roughness of the contact zone and high precision of work. When using machines for industrial purposes, the workpieces undergo primary temperature and mechanical treatment, so the allowance is minimal.
The capabilities of the machines are limited by performance characteristics. Using standard equipment it is impossible to work with parts whose taper exceeds 6º. The design of modern machines makes it possible to process the outer surface of any workpiece due to the design of the front and grinding headstocks, which can rotate around their axis.
As a rule, cylindrical grinding machines are used at the finishing stage of processing.
Modern machines have a number of additions:
There are 2 or 3 grinding wheels on one spindle. This allows you to carry out different processing without stopping and changing tools. Changing the grinding wheel that will now be processed occurs by rotating the “head”.
The machine may have a feeler gauge to determine the starting position of grinding and check the resulting size of the part after processing.
Automatic balancing of the grinding wheel, which greatly simplifies setup and makes the grinding process more accurate.
Automatic editing when a certain load on the spindle is reached. An extremely useful device for both finishing and roughing.
Main technical characteristics of the cylindrical grinding machine
Possible maximum permissible dimensions, as well as the weight of the workpiece;
Possible diameters of grinding processing, namely maximum and minimum.
Grinding machine work table parameters:
Possible table offset or maximum processing length;
Possible high speed;
Possible angles of rotation counterclockwise and clockwise of the grinding wheel spindle.
Important equipment parameters and technical specifications
The main parameters are indicated in the manufacturer's passport. These include:
- Electric drive power. The performance of the device depends on the value of this parameter. The unit of measurement is kW.
- Voltage. Defines the scope of use. Compact models for household work operate on a home network with a voltage of 220 V. Industrial machines operate on a voltage of 380 V.
- Desk dimensions. Limit the dimensions of processed workpieces.
- Maximum grinding wheel diameter. Its dimensions are determined by the interstate standard.
- Nominal speed. The rotation speed of the tool depends on this indicator.
- Availability of CNC and precision processing. Numerical program control allows you to increase the accuracy of the work performed, but the cost of such devices is quite high.
-Profile
During this grinding process, the work table moves along two coordinates. Thus, you can get not very smooth angles when transitioning from one treated surface to another. When using CNC it is possible to obtain radii with small risks.
Processing on cylindrical grinding machines is carried out using a method in which for each revolution of the workpiece being processed, a certain allowance is removed, called the depth of cut. This value does not remain constant; it changes throughout the entire operation and determines the structure of the grinding work cycle, the main stages of which are: rapid approach of the wheel until it touches the workpiece; cutting the circle into the workpiece; removing the main part of the allowance; nursing; quick withdrawal of the circle.
The equipment of cylindrical grinding machines depends on the capabilities of the machine, the properties of the material being processed, the requirements for processing accuracy, the location of surfaces, the level of surface microroughness after processing, as well as the cutting tool.
Cylindrical grinding machines can be equipped with magnetic tables for processing steel workpieces. Thanks to the magnetic table, multiple workpieces can be mounted, which significantly increases productivity by reducing the time for setting up and removing the workpiece compared to clamping with jaws.
Also, when using a magnetic table, the workpiece will expand evenly during processing, in contrast to the workpiece clamped in the jaws, which, due to the clamping force, will be deformed during expansion due to heating during processing.
Plunge-type cylindrical grinding machines have only one feed directed perpendicular to the surface being processed, their design is more simplified, and their design is characterized by increased rigidity to reduce vibration.
A plunge grinding cycle often begins with a roughing operation to remove a layer of metal, which should remove about 0.9 of the stock. Afterwards, finishing grinding occurs, which is performed at a low feed speed. As a result, after this operation, the entire allowance is removed.
After the final finishing operation, the cross feed stops and the workpiece continues to rotate, so-called nursing, until the sparks stop completely. At the end of the cycle, the grinding wheel is withdrawn and a new workpiece is installed for the next processing cycle.
A bad feature of plunge grinding is the release of a large amount of heat due to the large contact area of the grinding wheel with the surface being processed. Therefore, this type of processing requires plenty of cooling.
During the grinding process, the abrasive wheel may become dull, which negatively affects its cutting properties and the quality of the work performed. Tool dulling usually manifests itself in the form of intermittent sparking, increased noise, reduced workpiece surface quality, etc. In such cases, the feed is reduced and the circle is adjusted.
Grinding wear is the dulling and leveling or smoothing of the surface of the working cutting grains of the tool. If the grains are not visible to the eye, the pores are clogged with metal dust and shavings, then the grinding wheel must be adjusted and sharpened. Otherwise, it is impossible to complete the main task (process a workpiece or part) correctly.
The abrasive grains on the surface of the wheel experience thermal as well as physical stress (due to physical contact with the material). This is how the grains wear out, wear areas appear, the pores of the wheel become clogged with dust and microparticles of the used product, microparticles chip off, and abrasive grains can break out of the bond. These moments are the wear of the consumable tool, which lead to a decrease in the volume and weight of the circle. Which leads to a shift in the center of gravity and errors in wheel rotation during processing and, consequently, a decrease in processing accuracy.
The grinding wheel can become dull due to chipping of micrograins, become greasy, or self-sharpen. The first two options do not greatly change the shape and size of the disk, but lead to its poor performance. Therefore, such circles should be frequently adjusted and accuracy adjusted.
Plunge grinding is used for rough and fine grinding of cylindrical workpieces. When finishing grinding, in contrast to rough grinding, one strives to achieve the required shape and level of microroughness of the ground surface. Grinding is carried out with one wide circle, the height of which is one or one and a half millimeters of the length of the surface being sanded. Workpiece without longitudinal feed; The movement of the transverse feed of the grinding wheel to a given depth is carried out continuously or periodically.
To obtain a surface with less shape deviation and roughness, the grinding wheel is given additional axial oscillatory (oscillating) movement (up to three mm) to the left and right.
This method of processing a workpiece has the following advantages compared to the grinding method with longitudinal strokes: the wheel feed movement is continuous; you can grind shaped workpieces with a profiled grinding wheel; You can install two or three grinding wheels on the machine spindle and grind several sections of the workpiece at the same time.
Disadvantages of the cutting method:
Due to high performance, a large amount of heat is generated; the wheel and workpiece heat up more than during conventional grinding, so grinding must be carried out with plenty of cooling; it is necessary to frequently adjust the circle due to the rapid distortion of its geometric shape.
To transition from rapid approach of the circle (2000...3000 mm/min) to its plunge (five or ten mm/min), the feed speed of the circle must be sharply reduced. To avoid impact when the wheel comes into contact with the workpiece, an intermediate reduction in the wheel feed speed is carried out or the plunge section is lengthened with the beginning of contact after a certain delay.
The plunge-in stage is characterized by an accelerated transverse feed of the circle, causing a continuous increase in the cutting depth m. Due to elastic push-ups and gap selection in the technological system of the machine, the actual metal removal is less than that corresponding to the specified transverse feed, but as the tension in the system increases, this discrepancy decreases and the depth continuously increases cutting etc. To reduce the cutting period, an accelerated wheel feed is used, four or five times higher than the roughing feed.
In conditions of serial and mass production, when the grinding cycle is automated, fluctuations in the processing allowance cause various elastic compressions in the technological system and change the nature of the working cycle, which leads to different residual tensions of the system at the drying stage and has a noticeable effect on the final values of accuracy and roughness surfaces.
Roughing (roughing) grinding involves processing without a preliminary turning operation with the removal of an increased (from 1 mm or more) allowance for the diameter. It is advisable to perform this operation in power and high-speed grinding modes at 50...60 m/s. Unlike turning, rough grinding provides higher accuracy (8...9 grade) and lower surface roughness of 2.5...5 microns, and does not require subsequent preliminary grinding. Its use is advisable when there are precision workpieces or workpieces that are difficult to process with a blade tool.
Pre-grinding is usually performed after turning at high cutting speed (40...60 m/s). It is carried out before heat treatment to create base surfaces or as an intermediate operation to prepare the surface for final processing. Pre-grinding achieves accuracy corresponding to grades 6...9 and surface roughness of 1.2...2.5 microns.
Final grinding makes it possible to obtain surfaces with an accuracy corresponding to 5...6 grades and a roughness of 0.2...1.2 microns. Most often this operation is performed at a speed of 35...40 m/s.
Fine grinding is used mainly to obtain a surface with a roughness of 0.025...0.1 microns. It requires very good preliminary preparation, since the allowance removed does not exceed 0.05...0.1 mm per diameter.
Fine grinding is only possible with a precision machine and special wheels.
Its use is economically feasible only in conditions of single and small-scale production. In mass production, low surface roughness is achieved more efficiently and reliably on superfinishing and polishing machines.
Combining preliminary and final grinding is advisable if you have a machine operating in an automatic cycle, with forced automatic wheel dressing and the possibility of wide automatic control of grinding modes. An example is the grinding of the connecting rod journals of the crankshaft, where in one operation an allowance of up to 1...1.5 mm per diameter is removed; at the same time, the initial shape error is eliminated from 0.3...0.5 mm to 10 microns, the surface roughness of 80 microns is reduced to 0.4 microns and the dimensional accuracy is increased from 0.2...0.3 mm to 25 microns.
Destruction of the grains of the circle.
As they become dull, the grinding grains cut into the metal with more and more force. At this moment, when the force exceeds the strength of the grain or the ligament holding it, the grain will collapse or completely crumble.
Also, the disadvantages of grinding include high costs and
Temperature effect. When grinding at high speeds, an increased amount of heat is generated than when cutting with other tools. The rotation speed of the wheel during grinding is much higher than the cutting speed with cutters. The abrasive grains have negative rake angles, which complicates the cutting process.
The low ability of the wheel to perceive heat contributes to almost complete transfer of heat into the workpiece. The instantaneous temperature on the surface of the part in the contact zone reaches 1000°C or more. This leads to a change in the structure and physical properties of the metal.
Liquation is caused by a thermal effect. It appears as purple-colored grinding burns and grinding cracks. Grinding burn-through is understood as a local change in the structure of the surface layer of the sanded part in the direction of deterioration in its quality - the hardness and wear resistance of the surface layer.
Principle of operation
There are several methods of external processing, which depend on the technical parameters of metalworking equipment.
In repair shops, the longitudinal grinding method is most often used. In this case, the workpiece to be processed must be secured in the centers of the machine. An electric motor rotates the headstock along with the fixed object. Longitudinal movement is performed by the feed mechanism, changing the position of the workpiece relative to the grinding wheel.
In addition to longitudinal grinding, the following processing methods can be performed on modern machines:
- Deep. The amount of allowance in one pass can reach 0.4 mm of metal. The impact on the surface is carried out by the conical part of the tool.
- Mortise. This technology involves the use of wide grinding wheels to perform roughing or finishing work. During processing, the position of the workpiece relative to the circle does not change.
- Ledges. The method combines deep-feed and plunge grinding. This makes it possible to process products of complex shapes.
Classification
Depending on the dimensions, productivity, type of installation, there are two groups of CNC cylindrical grinding machines:
- Tabletop models. Compact equipment that is used in private workshops. They are characterized by low performance, small dimensions, and a small number of additional functions. They are powered by 220 volts. Most desktop machines come with manual controls without CNC.
- Industrial models. Large machines that are equipped with a powerful motor, a large work table, guides, and stepper motors. There are machines with two or more working parts. Industrial equipment has a high productivity rate and is therefore suitable for mass production. Most models are powered by 380 volts.
Depending on the functionality, there are two groups of cylindrical grinding machines:
- Simple machines. Designed to carry out one technological process. You can assemble such devices with your own hands by looking at ready-made drawings and preparing consumables and tools.
- Universal models. Multifunctional machines with different configuration options. Thanks to this, it becomes possible to process workpieces of complex shapes and different sizes.
CNC Cylindrical Grinder
Classification
Certain points indicated in the drawing and passport determine the following classification of grinding equipment:
- Universal ones have a rotating work table, it is possible to rotate the workpiece and the grinding wheel itself. The universal version is equipped with an additional headstock.
- Simple ones allow you to process only certain workpieces.
Numerical program control allows you to increase the degree of automation of work several times. Let us highlight the following points:
- High grinding precision. The mechanism that is used to fasten and feed the wheel, when automatically fed, allows you to obtain dimensions that can have a deviation of only a few hundredths of a millimeter.
- Productivity is significantly improved. Most of the stages of the technological process are performed automatically, which means they do not require operator intervention.
- The likelihood of marriage is reduced. Reducing how many steps a person has to perform can reduce the likelihood of problems occurring.
- Costs are reduced due to the fact that one operator can service several workstations.
A CNC cylindrical grinding machine is quite rare, as it is used in rare cases in large-scale and mass production. The cost due to the inclusion of a numerical control system in the design increases significantly, so it should be used only for large-scale production.