Types of cutting discs
metal disc from Vulcan
Among the many consumables for grinders, the most common are metal cutting discs. They are somewhat cheaper than their stone or concrete counterparts and are usually painted blue. The difference lies in the type of abrasive material: coarse chips or crushed diamond. To polish metal, special nozzles coated with fabric are used.
Consumables vary in size, thickness, coding and price. All this data is indicated on the front surface of the cutting disc.
Typical disk sizes for angle grinders
All interchangeable wheels have standardized sizes, so for any model of grinder you can choose a suitable size disk, even if it is “non-original” (from another company). The table below shows the typical dimensions of cutting discs in terms of thickness, diameter of the circle and seat:
| Circle diameter, mm | Thickness, mm | Mounting socket, mm |
| 115 | 1,0; 1,6; 2,0; 2,5; 3,0; 3,2 | 22,00; 22,23 |
| 125 | 0,8; 1,0; 1,25; 1,6; 2,0; 2,5; 3,0; 3,2 | 13,20; 22,23 |
| 150 | 0,8; 1,0; 1,25; 1,6; 2,0; 2,5; 3,0; 3,2 | 13,20; 22,23 |
| 180 | 1,0; 1,25; 1,6; 2,0; 2,5; 3,0; 3,2; 4,0 | 22,23; 32,00 |
| 230 | 1,6; 2,0; 2,5; 3,0; 3,2; 4,0 | 22,23; 32,00 |
The larger the diameter of the circle and its thickness, the thicker the products it can cut. Please note that the diameter of the disc should not exceed the permissible size for a particular grinder model. Thus, a 230 mm disc cannot be placed on an angle grinder with a maximum allowable wheel size of 125 mm. Such actions will force you to remove the protection, which is a violation of safety regulations, and will lead to an increase in the linear speed of the cutting edge, which is why the disk can simply fly apart during operation and injure the operator.
The diameter of the seat in most grinders is 22.23 mm, 13.20 mm is less common, and the diameter of 32.00 is relevant only for large disks. Pay attention also to the linear speed of rotation of the disk. For example, if the disc’s marking indicates a speed of 13,000 rpm, this means that your grinder must also produce such revolutions in order to work with it.
You can understand what material the nozzle can work with and what its typical dimensions are by looking at its markings on the front side. If you came to the store and picked up the disc, you can see the following:
We would like to note that sometimes the buyer may encounter non-standard nozzle sizes, and this may apply to both diameter and thickness. This often happens when purchasing “no-name” disks of unknown manufacture. We still recommend buying branded discs, since unknown ones are erased faster, and in the end you have to pay more.
Selection by size
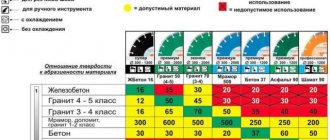
The outer and inner diameters of the circle are indicated on the main surface of the consumable. There are 9 standard external sizes from 125 to 500. The indicator is selected taking into account the class of the angle grinder. It is strictly forbidden to work with a larger circle. Only for large professional tools can you purchase consumables of any diameter.
The inner or bore diameter must match the size of the drive shaft. Most shafts are produced with a diameter of 22 mm, so 22.2 mm is an almost universal mounting diameter. Both sizes must fit the instrument model!
Selection by thickness
It's much easier to cut with a thin circle. Indeed, when cutting into metal, a thick cutting disc experiences powerful resistance; more effort will be required to overcome it.
The cut with a thin disk is more accurate, and the work goes faster. The working surface heats up less, so it lasts longer. Thin circles are considered to be up to 1.2 mm thick, compared to the standard 2.4-2.5 mm with a diameter of 125 mm. The thickness of the disc is directly proportional to the diameter!
This option is suitable for small grinders with batteries or low power, allowing you to save energy.
There is an opinion: the thinner the consumable, the more fragile it is. This is nothing more than a myth. Any cutting disc is reinforced from the inside with non-woven fabric, so the safety of work depends on compliance with the rules, and not on the thickness of the consumable.
Encoding
The circle specification is encoded in four characters, Latin letters and numbers:
- the first letter indicates the material of the abrasive chips: AS - white electrocorundum, it is suitable for working on stainless steel, because the alloy contains practically no chlorine, sulfur and iron, which increase the cutting temperature; A - electrocorundum; C - silicon carbide - such circles are used to cut tiles and stone, but not metal;
- number - indicates the number of abrasive grains per unit area. The higher the number, the smaller the particle size. For cutting steel, larger grains are used - 24, 30; for working on soft non-ferrous metals, smaller ones - 60 or 40;
- the Latin letter is the hardness of the ligament. The first letters of the alphabet are the softest letters, the further from the beginning the harder. The softest bonds are selected for processing the hardest metals! You need to know this important ratio when choosing consumables for an angle grinder. During cutting, worn particles fall off and new ones, not yet dulled, come into play. If the bond is too tight, the cutting disc becomes “greasy”: it heats the metal and makes cutting difficult. At the same time, a circle with an overly soft bond wears down faster;
- the last Latin letter (or pair) is the name of the binding material, most often bakelite. Denoted as BF.
Specification
In the form of a four-digit code.
It encrypts the parameters of the cutting grains and binder - the main elements that make up the abrasive wheel.
Its specification depends on these parameters. How to read the code - for example "A 30 S BF"?
Pictured: AC-D SP cutting disc from Hilti.
- The first letter is the material of the abrasive grains: A - electrocorundum, AS - white electrocorundum, which is maximally purified from iron, sulfur and chlorine, and therefore does not strongly burn the workpiece, which is important for cutting stainless steel. “C” (silicon carbide) is also found. It is used to make grains for stone laps.
- The number indicates the abrasive fraction. For steel, large grains are used (24 or 30), and for non-ferrous metals, smaller grains are used (40 or 60).
- The next symbol shows the hardness of the ligament. The higher the serial number of the letter in the alphabet, the stronger the ligament. It is important to know here that the hardness of the material being cut and the strength of the bond have an inverse relationship. It is important to choose the optimal ratio. During the cutting process, dull grains should crumble and give way to new cutting elements. If the bond is too hard, the wheel becomes greasy, making it difficult to cut and overheating the workpiece. On the other hand, a disc with a bond that is too soft will wear down quickly.
- Lastly, BF is Bakelite. It is this that, as a rule, serves as a binding material.
Images used in this article: bosch-professional.com, hilti.ru, milwaukeetool.ru
Price and manufacturers
metal disc from Hitachi
For rare household jobs, cutting discs from the low price category are quite suitable: “Sparta”, “Zubr”, “Tsentroinstrument”. With occasional use they will last quite a long time.
The quality of the abrasive material is not bad, the price is reasonable. The main thing when working with consumables of this class is not to work for a long time without breaks. If the circle stops sawing, it is cleaned with red or yellow brick.
Professional metal discs cost 3 times more. But only they are suitable for industrial use. These are consumables, “Distar”, “Hitachi”. They withstand daily work with the most difficult materials. Professional circles, as a rule, are intended to work with a specific material: reinforced concrete, granite, tiles, steel, non-ferrous metals.
Video with a metal cutting disc test:
Types of cutting abrasive wheels
Today, different criteria are used to classify cutting discs into types. Let's consider only the most popular.
Purpose
Based on the “sphere of purpose” criterion, abrasive wheels form the following groups:
- discs for stone processing. They are used for cutting objects made of asbestos-cement sheets (both flat and wavy), for cutting paving stones, paving porcelain tiles, non-cracked bricks and stone structures;
- circles for working with metal. Used for cutting steel plates, shaped metal products (for example, channels), metal angles, profile pipe products, construction fittings;
- cutting discs for wood. In addition to wood products and products of its processing (for example, MDF boards), they are used for cutting gypsum plasterboard (an abbreviation of the phrase Plasterboard Sheet), plastic components of window profiles, as well as pipes made from high-strength polymer.
Production technology
According to the “production technology” criterion, cutting wheels are divided into 2 main types.
Abrasive discs
A consumable tool for metal processing includes two layers of fiberglass mesh, between which there is a mass including abrasive particles made from the following materials:
- superhard electrocorundum;
- carbocorundum – this is the abbreviated name for silicon carbide;
- corundum – alumina with the following chemical formula: Al2O3
One of the mandatory stages in the production of abrasive wheels used when working with metal is heat treatment. After this, the product becomes highly resistant to irreversible destruction. The baking temperature for the circle is +200°C.
Diamond discs
They are mainly used for cutting materials with particularly high strength characteristics. This:
- hard fine-grained concrete grades from M600 to M1000;
- natural stone granite;
- a rock known as marble;
- clinker brick;
- frozen asphalt.
Steel alloys are used for production. An abrasive mixture containing diamond crumbs/particles is applied to the surface of the end of the disc. The width of the diamond-containing layer usually takes values from the range min 1.50 mm, max 3.0 mm
There are three types of cutting tools on the market.
- The discs are solid. With their help, wet cutting of material is carried out. They look like a solid circle, the diamond edge of which is not interrupted.
- Segmented disks. Used for dry slicing. The cutting edge, filled with diamond particles, is a collection of individual equally spaced segments.
- Turbo disc. It is a universal type wheel: it can carry out dry cutting, as well as cutting with water cooling, that is, wet. This property is ensured by the following design feature of this consumable tool: the diamond-containing edge is made in the form of a wave. This makes natural cooling possible.
Review and comparison of cutting wheels
| Model | Outer diameter, mm | Thickness, mm | Price, rub |
| LUGA-ABRAZIV 115Х1.6Х22 А40 | 115 | 1,6 | 17 |
| KRATON 1 07 02 026 | 115 | 1,6 | 23 |
| ATTACK 1458910 | 125 | 1,6 | 56 |
| DEWALT DT42301-XJ | 125 | 3 | 89 |
| BOSCH Expert for Inox 180Х2,0Х22 | 180 | 2 | 110 |
| STOMER CD-230T | 230 | 1,8 | 235 |
LUGA-ABRAZIV
CRATON
ATTACK
DEWALT
BOSCH
STOMER