What is a sewer protection zone? Every person in his life has at least once encountered a warning sign “Security zone”. Especially often, such signs are installed in places where cable networks are laid, storm sewers, near reservoirs and water supply systems.
There is also a sign that indicates a “sewer protection zone.” By the way, even people who deal with the installation of a drainage system on a daily basis may not know about the existence of such a sign. And even more so, the question about the need for such a warning is asked by ordinary people who are in no way connected with the installation of sewerage systems. And they often suffer from their ignorance.
What is a sewer protection zone?
The sewerage security zone provides complete security for various objects. The biggest problem is caused by the water supply, which can completely deteriorate if the well is placed incorrectly. The system must be at a certain distance. So calculations are a prerequisite for the work of professionals.
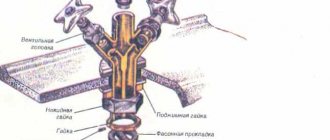
Even when creating a pressure sewer, GOST must be taken into account . Its data is mandatory, so the pipe must pass in a certain place. For this reason, experts advise taking the numbers seriously, because the INSTALLATION of the well will easily indicate its location.
What is prohibited from doing in the sewer security zone?
Protected zones of water supply and sewerage forces us to take the work carried out seriously. The laying of the pipeline does not subsequently force one to take into account the standards and refuse some actions. What is it about?
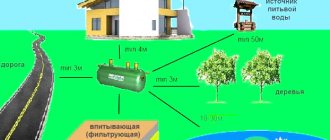
- Trees are planted at a distance of 3 meters from the collectors;
- Soil cannot be removed or added;
- The construction of landfills and storage buildings is excluded;
- Piling and blasting operations are prohibited;
- The use of drilling and impact rigs is prohibited;
- Access to structures must remain open;
- Construction work is carried out under a special permit.
When closed storm sewer is installed, SNiP reminds you of certain requirements. If laying sewer networks , the work immediately becomes more complicated. These actions must be performed strictly, because the rule allows you to avoid damage to the finished pipeline.
What happens if requirements are violated?
When storm drain protection zones are not taken into account when performing other work, serious problems arise. Some of them appear instantly, while others appear over time. In any case, a person should take these issues seriously, as they often turn out to be critical.
- Pipeline rupture;
- Well collapse ;
- Changing the angle of inclination.
Such problems cannot be eliminated without serious repair work. Because of this, the security zone of any sewer must be taken into account by professionals. They eliminate possible troubles to ensure stable operation of the entire system.
What features are taken into account when calculating the security zone?
How many meters should you leave to the water source? Foundation? People try to find answers to these questions on the Internet, but they only need to refer to established standards. So, the INSTALLATION of a well tells you at what distance from it the sewerage system should be located. What environmental parameters are used for calculations?
- Seismological activity;
- Average temperatures;
- Available humidity indicators;
- Soil characteristics.
Today, the simplest drainage system is based on the data presented. They are shown for different regions, so it’s easiest to check with professionals for details.
If this is not possible, USTAN and GOSTs will come to the rescue. Using the data from them, it will be possible to draw certain conclusions that will allow you to quickly carry out the required work.
Distances to various objects
The SETUP of the well suggests that the location of objects must be certain. It is necessary to correctly select the optimal locations in advance, guided by the project, so as not to make serious mistakes. It is necessary to address various conditions, highlighting the most significant indicators.
Communications within the city
The most difficult thing is to lay main pipeline in an urban environment. Dense buildings do not allow free choice of location, so communication designers have to make careful calculations. What distances have to be taken into account?
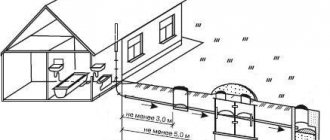
- Depending on the diameter of the pipes, the distance to the water supply varies from 1.5 to 5 meters;
- To the storm sewer - 0.4 meters;
- Depending on the pressure in the gas pipeline, the distance varies from 1 to 5 meters;
- Heating networks are 1 meter away.
The requirements are specified based on current SNiPs. A defined protected object provides the necessary input data, which is applied in practice, giving accurate indicators for subsequent location.
This information remains fundamental for professionals. They are based on it, so even in urban environments new communications appear regularly.
Longitudinal arrangement of water supply and sewerage
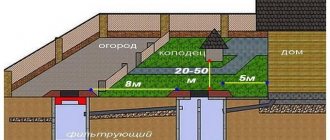
The longitudinal arrangement of rainwater drainage and water supply is also described by USTAN . It suggests where the system can be installed based solely on the diameter of the pipes. What data should you remember?
- Diameter 1 meter – 10 meters;
- More than 1 meter – 20 meters;
- Laying in wet ground – 50 meters.
The specified data is permanent. Connivance is not allowed, as it can negatively affect the water supply. Accordingly, installation is carried out taking into account strict requirements.
Sewage networks cannot be laid in sanitary areas of main water pipelines.
Sewer protection zone: the law is on guard
Everyone has come across signs “Cable Protection Zone” or “Reservoir Sanitary Protection Zone” in life. But not even all builders know that there is also a sewerage protection zone.
At first glance, the question is logical: “What is there to protect?” However, sometimes this ignorance can lead to unpleasant consequences - both for owners of private houses and for officials of various installation organizations.
Damage to external sewer networks is not such a rare occurrence. And it occurs with a frequency even greater than on water supply, electricity or communications mains.
In this regard, excavation workers - both legal entities and owners of private landholdings, when digging trenches for the installation of sewer pipes and pits, have a greater risk of causing damage to the drainage system than other communications
The responsibilities of owners and operating organizations to install warning signs about the passage of underground cables or pipelines in a given location, or the border of the sanitary zone of a reservoir, are expressly stated in regulations. In the case of water management, this is the Water Code. The rest contain special Laws and Regulations.
And only for the sewerage system such requirements are not regulated. As a result, if other communications are damaged, but there was no warning information in this area, the responsibility lies with the one who did not install the sign. And the work contractor is to blame if there was a corresponding sign, but he ignored it.
The situation with drainage pipelines is much more complicated. Here, for some reason, legislators have not established clear standards, and network owners are not required to somehow designate sewer security zones. However, from a legal point of view, damage to sewerage equipment is an administrative offense.
Note! The Administrative Code states: “Article 7.7. Damage to objects and systems of water supply, sewerage, hydraulic structures, devices and installations for water management and water protection purposes
Damage to objects and systems of water supply, sewerage, hydraulic structures, devices and installations for water management and water protection purposes entails the imposition of an administrative fine on citizens in the amount of one thousand to one thousand five hundred rubles; for officials - from two thousand to three thousand rubles; for legal entities - from twenty thousand to thirty thousand rubles.”
It should be noted that the article only talks about direct damage to water supply and sewerage systems and structures. If at the same time there are harmful effects on the environment, this will be another offense, perhaps more than one. And the perpetrator will have to compensate for the damage caused.
So it is quite possible, while minding your own business and not intending anything bad, to get into serious trouble.
Precautionary measures
Considering the possible negative consequences, it is worth trying to prevent their occurrence. When planning to carry out excavation work, you should study the surrounding area.
The main sign of the presence of different types of sewer pipes is manhole covers with a characteristic large letter “K”. It can also be given away by coordinate plates or paint markings.
But even if they are not found, it is better to play it safe and contact your local water utility. There are diagrams of all sewer lines, which indicate whether or not a security zone of a sewer collector or other structure is located in a given area.
Moreover, in order to avoid subsequent inconsistencies, it is better to ask for a certified copy of the plan. If it turns out that the security zone is still present there, you can immediately apply for a permit to carry out work. Without such permission, work cannot be carried out near the sewerage system.
What is the security zone of the sewerage system according to snip?
Sanitary protection zones for water supply facilities are spaces that allow the protection of aquifers and adjacent soils from polluting factors, as well as contributing to the complete safety of technical structures. Options for the parameters of such safety belts are described in detail in SanPiN 2.14.1110-02.
After an artesian well is drilled, water quality tests need to be done. The following parameters are checked:
- Organoleptic and physical properties of drinking water: taste, color, degree of transparency, presence of various inclusions.
- Chemical composition, presence of inorganic and organic compounds, their concentration.
- Radiometric control, absence of dangerous isotopes.
- Microbiological composition, the presence of pathogenic bacteria, viruses, protozoa.
The conclusion is issued by the territorial division of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision. If there are no deviations from sanitary standards in all research protocols conducted by a certified laboratory, the water is recognized as suitable for drinking and cooking.
If minor inconsistencies with the requirements are identified, the operation of the well is allowed only as a source of water for technical needs.
Security zone of the water pipeline (water pipeline): how many meters from the underground pipeline, SNiP and SP
The security zone of the water supply system is a special term for determining the required distance from the water supply system, water conduit and water intake, which is subject to strict compliance with SNiP and SP standards.
The main current distancing standards were developed on the basis of conducted and recorded scientific research in the field of sanitation and hygiene - SanPiN. Protection zones are aimed at preventing contamination of water sources.
SNiP and its updated version - SP - determine the distance of water supply facilities from potential threats.
What is a protected area
A security zone is one of the types of zones with special conditions for the operation or protection of certain territories, the size and content of which are regulated by the current legislation of the Russian Federation. The concept of a protected area includes:
- actually, security (ensuring the integrity and absence of damage to both the structure itself and the potential harm that the object protected by fencing or legal norms may cause;
- the sanitary protection zone performs a dual function - sanitary, anti-epidemiological and protective - protection and removal from structures that pose a potential threat of damage;
- water protection zones that prevent pollution of water bodies from which the population is likely to be supplied with water;
- sanitary protection zones for sources of drinking water and liquids for household supplies;
- other protection zones - near airfields, floods, protected cultural and historical sites.
The goals of legislative restrictions carried out at the federal level are to approve special operating conditions or exclude them from use other than for their intended purpose. The distance at which objects should be located from areas of cultural or historical heritage may be determined by a regional government decree.
Fishing and water protection territories and their delimitation are fixed at the level of federal legislation. How many meters in each direction is the security zone of gas and oil pipelines, oil product and ammonia pipelines, pipelines to fully satisfy the household needs of the population is determined by the relevant SNiP, SanPiN and SP.
Sanitary standards for water pipes
According to sanitary standards and rules, the sanitary zone is the distance that must be maintained from any pipe in which water is transported. Moreover, regardless of its personal or state affiliation, whether it is filled from underground or above-ground sources.
The sanitary zone of the water supply is a distance that must be observed to prevent potential contamination of water supply networks or other sources of water supply.
Since SanPiN, which defines the protective territory, was created on the basis of Federal Law No. 52, non-compliance with the requirements threatens serious troubles for violators of existing rules. In this regard, it is worth noting the following:
- missing or created in violation of existing standards, protected areas and sanitary water supply zones are punishable by a fine, often quite significant for the budget;
- the operation of communications, in accordance with existing regulations, is regulated by the Code of Administrative Offenses (CAO);
- Violation of sanitary zones of reservoirs and other water supply sources can amount to up to 40 thousand rubles for legal entities, and up to 2 thousand rubles for individuals. and more depending on the severity of the offense committed;
- the water supply area cannot be used for any type of construction or reconstruction, unless we are talking about structures that are directly important for its functioning or protective measures of a sanitary and epidemiological nature;
- the water supply zone presupposes the absence in the immediate vicinity of sewerage, wastewater, and agricultural land in which pesticides are used;
- Strict restrictions are imposed on proximity to garbage dumps, burial of any type of waste, and even on logging, unless it is unsanitary.
Regulatory documents for water pipelines
The basic requirements and standards are set out in SanPiN 2.1.4.1110-02. They were developed with the participation of MMA named after. Sechenov, the Russian Ministry of Health and the Russian Ministry of Justice.
Construction of water supply networks
It is in this document that you can find definitions of underground and surface source protection zones, general requirements and individual measures for the protected area. This is the correct determination of how many meters it is, maintenance in optimal condition, a ban on construction work, warning signs and much more.
The main standards for protected areas during the construction of water pipelines are collected in the following regulatory documents:
- SP 18.13330.2011 “General plans”. It provides for compliance with all necessary requirements when developing projects for industrial enterprises, in accordance with the paragraphs of Federal Law No. 184 “On Technical Regulation”.
- SP 31.13330.2012, which is a revision of the famous SNiP 2.04.02-84 under the same name, developed by the USSR State Construction Committee, based on many years of practical experience and state-funded scientific research.
- SP 42.13330.2011, approved by the Ministry of Regional Development of Russia, known as urban planning standards. It contains standards for distancing and designing drinking water sources, as well as water supplied for technical needs in populated areas.
- SP 42.13330.2016, approved in 2021 and entered into force in 2021, which took into account all the requirements of new times and changes in legislation. As well as the complicated environmental situation in areas with significant concentrations of houses and people.
Main pipeline
Subtleties of water supply construction
According to adopted resolutions, construction rules, revised from previously adopted SNiP, specialists are required to take into account the most variable parameters.
in particular, temperature and climatic conditions, existing chemical processes in the service area, the survival time of pathogenic microorganisms in the natural environment.
They also take into account the main technical indicators of the water supply system, its placement and the degree of protection from damage. Based on all these parameters, a security zone is established for each segment of the water transportation network to the consumer.
Installation of water supply on fixed supports
The ZSO standardly consists of three sanitary protection belts - strict, restrictive and observational. The security zone of water supply networks depends on the nature of the source, to which either 500 or 1000 m can be added at each subsequent belt. Everything depends on certain parameters indicated in the table above.
Sewer security zone
Domestic waste poses a risk to water supplies and the environment. That is why such a concept as a security zone of sewer networks appeared. SNiP specifies the size of the protected area and designation parameters. This area not only serves to protect water and soil, but also to protect the sewer pipeline from damage.
Therefore, construction, tree planting and other work are prohibited in the protected zone. Sometimes you can see a sign stating that there is a security zone located here, for example an electrical cable. Any type of earthwork is prohibited in this zone.
The sewerage security zone, unlike communication or electricity cables, for some reason does not have a visual marking. This may be a consequence of legislators' shortcomings, but the law provides for liability for damage to sewer systems (Article 7.7 of the Code of Administrative Offenses) in the form of substantial fines.
And if damage to the sewer system leads to contamination of the soil or drinking water, then it is possible to initiate a criminal case against the culprit of the accident.
General concept - security zone of sewer networks
A security zone is the area surrounding any communications, in our case, external sewerage. Within this territory you should not perform the following actions:
- planting green spaces;
- storage of building materials;
- waste storage;
- earthworks - holes, trenches, etc. ;
- cutting or adding soil;
- construction;
- unauthorized construction of a roadway, even temporary from concrete slabs;
- obstruction of free passage to communications.
The boundary of the protection zone is determined by the Ministry of Environmental Protection, and exact data can be found in the local department responsible for wastewater disposal.
Dimensions
The sanitary zoning of the security zone around water pipelines can be divided into three security zones.
The main strict regime sanitary zone is located around the water intake site in accordance with paragraph 1.5 of SanPiN .
Its purpose is to protect the source of water supply from destruction or contamination.
The second and third belts around the water intake source are designed to prevent the possibility of contamination.
Boundaries of the first belt for a surface water supply source
The boundaries of the first belt are established as follows. For flowing sources (rivers and canals) from 200 meters upstream, and 100 meters downstream. Along the shore adjacent to the water intake point from 100 meters, towards the opposite shore when the width of the water area is less than 100 meters, the entire water area and 50 meters along the opposite shore from the water line.
When water is withdrawn from a lake and reservoir, the boundaries of the first belt include a water area of 100 meters in all directions, along the adjacent shore 100 meters from the water line.
Boundaries of the second sanitary belt when drawing water from a river or canal
Upstream, based on the flow speed and water content, there is a 95% supply of water intake for a period of at least 5 days, downstream 250 meters.
The lateral boundaries of the protection zone for flat terrain are 500 meters and to the top of the first slope for mountainous terrain, but not more than 1000 meters.
If there is a reverse flow in the river, the distance of the boundary of the second zone of the protection zone to the water intake is determined by agreement with the sanitary service.
If there is navigation, the boundaries of the second belt include the water area up to the fairway.
Boundaries of the second sanitary zone for water intake from a lake or reservoir
From the water intake in the water area in all directions at least 3 km.
The number of winds should also be taken into account, in agreement with the sanitary station. Lateral boundaries are set in the same way as for a flowing water intake source.
Determination of the boundaries of the third sanitary zone when drawing water from a flowing source, lake or reservoir is established in the same way as for the second zone, lateral boundaries along the watershed, no more than 3 km from the watercourse or water area.
Determination when using underground sources
The boundaries of the first zone are determined from the point of water intake and are at least 30 or 50 meters in case of insufficient water protection.
For water intakes located in areas that exclude pollution, in agreement with local sanitary authorities, it is permissible to reduce the boundary of the first zone to 25 meters.
When using artificially filled underground sources and reservoirs, the boundaries of the zone are determined from infiltration structures and are more than 50 meters.
The boundaries of the second and third zones are determined with the calculation of possible microbial contamination of protected waters and are precisely determined by the sanitary service.
Determination of the boundaries of the protection zone of water pipelines
In practice, it is determined by clauses 2.4 of SanPiN.
The width of the sanitary protection zone around the water supply is determined at the extreme points and is 10 meters in both directions in accordance with SNiP.
You may need a cesspool for a private home, ways to maintain an autonomous drainage system with rare and inexpensive cleaning. Read this article about the drainage system around the house
And here is everything about water distribution in a private house. Connecting external and internal water supply to water supply sources.