The water that we are accustomed to, observing it in nature - streams, rivers, seas - is in a bioregulation system. Bacteria and aquatic plants purify water from dissolved substances, making it suitable for life of insects, fish, birds, animals and humans, of course.
When we take water from a well, a well, or any other underground source, we habitually expect to receive clean water.
However, iron, manganese, organic matter, hydrogen sulfide (these are the main pollutants, there are many others) make our water unsuitable for drinking and domestic needs.
Alas, the water of underground sources is rarely pure in our understanding.
Such water with a high content of pollutants:
- has a nasty smell
- nasty taste
- leaves indelible marks on plumbing fixtures,
- destroys steel parts of the water supply system,
- forms sediments that pollute the water supply
- and brings many other troubles
Pressure aeration is one of the most common methods for oxidizing dissolved metals, removing organic matter, hydrogen sulfide and ammonia.
What is aeration
This is the process of saturating water with oxygen (less often with ordinary air) for the purpose of purifying it. Such enrichment triggers natural chemical reactions, as a result of which dissolved impurities become oxides and precipitate, and this can then be relatively easily retained by trap filters and removed. After that, volatile compounds, toxic and unpleasantly smelling, are removed.
Using variations of the method, it is possible to effectively remove particles of metals (for example, iron or manganese), gases (hydrogen sulfide, chlorine, methane and others), carbon dioxide and organic compounds, as well as bacteria and viruses, from liquids.
Why is aeration needed?
With water purification you can:
- remove harmful salts from it;
- carry out its biological treatment;
- increase oxygen concentration;
- remove unpleasant and any foreign odors.
Please note that liquid with excessive iron content is unsuitable for drinking or cooking, because if consumed regularly, this excess will be deposited in the body and will gradually lead not just to poor health, but to chronic diseases, seriously compromising health. It is also not suitable for household purposes, since its salts will spoil the laundry during washing and generally settle on the internal surfaces of heating elements, pipes, and plumbing fixtures, gradually clogging all passages.
Water purification by aeration
Its advantage is that you can find your own approach in absolutely any case, focusing both on the final goal and on the current conditions: the volume of the working environment to be enriched, the current flow pressure and other important factors.
Naturally, the equipment used, productivity, and cost level directly depend on the chosen method. Therefore, you need to immediately decide why you are solving this issue, why you need the liquid - to service a cottage, a country house with several floors, a personal plot with greenhouses or an industrial facility.
Today there are 3 main methods - let's look at each of them in order.
Biological aeration
It is based on a natural phenomenon, which is that the oxygen level in water depends on the amount of phytoplankton in it, which directly produces 80-90% of all air in the working environment.
Hence the simple dependence: the more of these organisms, the sooner the enrichment will occur, which means their growth must be stimulated in every possible way. Why it is permissible to use a variety of approaches:
- add mineral fertilizers that activate natural metabolic processes;
- populate a body of water (aquarium, container) with fish that eat vegetation; for example, grass carp or silver carp, since they eat adult individuals, forcing the young to reproduce and at the same time generate oxygen.
The second option is also good because it has a complex effect. First of all, because not only phytoplankton is absorbed, but also detritus, which would certainly take some part of the air if it remained in the water. In this way, oxygen is not only produced, but also saved. In addition, the vegetation that prevented organisms useful to us from reproducing is also destroyed along the way, and it is eaten and does not die, and gas is also not spent on the processes of its decomposition. This is the case when indirect influence plays an extremely important role.
MBFT-75 Membrane for 75GPD
SF-mix Clack up to 0.8 m3/h
SF-mix Runxin up to 0.8 m3/h
Chemical aeration
This is an artificial method with a very simple principle: add reagents to the working environment that increase the activity of oxygen release. There are a lot of suitable substances, and examples include:
- hydrogen peroxide – H2O2;
- potassium permanganate – KMnO4;
- calcium peroxide – Ca2O;
- a number of others, less commonly used.
Here it is necessary to take into account that each such catalyst not only has its own degree of effectiveness, but also certain side effects. Thus, as a result of interaction with Ca2O, slaked lime is also formed, which accelerates the much-needed enrichment reaction.
To solve the issue chemically, you should add the calculated amount of the substance to the liquid. So, to release 1 liter of oxygen, you should add 4.6 kg of calcium peroxide.
The nuance is that the proportions must be strictly maintained: if the concentration is not maintained, the air simply will not be released in the required volume, but if it is exceeded, serious damage can be caused to both the local water supply system and the environment in general. Therefore, it is important to remember that each catalyst has its own proportions and adhere to them.
Mechanical aeration
The most used option is because it is carried out practically in a passive mode, almost without human intervention, and proceeds relatively quickly. In addition, it does not pose even a theoretical threat to the environment, and this is a key advantage on an industrial scale.
It is implemented quite simply - as follows:
- a table is installed in the container;
- it is supplied with a working medium from a pipe;
- falling, the liquid breaks, part of its drops flies to the surface, receives an air charge and returns to the reservoir.
Now we have presented the simplest saturation scheme, on the basis of which other, more complex solutions are improved and implemented. Examples include the well-known sprinkler systems, which are widely used to irrigate farmland and thus help grow various crops. In fish farms, special devices are also in demand, but only in cases where the inhabitants of rivers, lakes and ponds are more than 2.5 t/ha (according to calculated data).
The need for deferrization of water. Types of aeration cleaning
Aeration systems are widely used to purify water from iron for industrial and domestic purposes. A liquid rich in iron compounds, organic pollutants and volatile substances requires mandatory preliminary cleaning, which involves the oxidation of foreign inclusions. There are different methods of oxidation, but one of the most popular is aeration. Why? Because it is produced without the use of chemicals and is as safe as possible. Oxygen is used instead of dangerous chemicals.
The main purposes of using aeration of water from wells:
- removal of iron salts;
- elimination of foreign odors;
- biological treatment;
- increase in oxygen concentration.
How is aerated water produced?
In general, the process of enriching it with oxygen takes place in 3 stages - according to the following scheme:
1. The production of oxygen is stimulated (by the chosen method - chemical, biological or mechanical), triggering reactions as a result of which dissolved impurities are oxidized to a di- and trivalent state.
2. Foreign substances precipitate and are captured by filters (so that they do not accumulate on the bottom and walls of the container).
3. The gases remaining and released as a result of the interaction (ammonia, hydrogen sulfide, chlorine) are blown off.
Types of water aeration
In addition to ways to increase air concentration, there is a division according to a number of parameters. This includes the level of complexity of the equipment used and the nature of the reagents used. But there is one factor that stands out. This is a method of supplying oxygen, and, in accordance with it, there are two schemes - let’s move on to consider the first.
AMETHYST - 02 M Residential building for up to 10 people or up to 2 cubic meters/day.
Aeration unit AS-1054 VO-90
Main table dispenser AquaPro 919H/RO (hot and cold water)
Gravity
The short gist is this:
- The liquid enters the tank through nozzles (special nozzles), that is, with dispersion.
- As they fall, the droplets mix with the air contained in the atmosphere.
- At the same time, the membrane compressor also pumps oxygen at the bottom.
- Interacting, the molecules are oxidized, and the dissolved forms contained in the water precipitate and are removed by filters.
- The working medium is pumped out using a pump and supplied to the end points of consumption.
Installations operating on this principle are used when the liquid contains excess salts, hydrogen sulfide and methane, as well as in cases of excessive color and turbidity or the presence of an unpleasant aroma.
Non-pressure systems built on the basis of the method differ in size and performance, and while some of them are aimed at cottages and country houses, others will satisfy the needs of even large industrial enterprises. They are quite environmentally friendly and safe, so it is permissible to supplement their capabilities with reagent cleaning - in the presence of a serious excess of organic compounds and/or low pH levels.
Let's move on to the second scheme.
Nadornaya
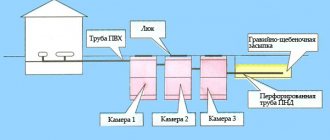
The most widespread technology - due to its economic profitability, speed of implementation and complete absence of harm to the environment. This is implemented in the following way:
1. Water is taken from the source and then supplied to the inlet of the purification column through a flow sensor.
2. Having received the appropriate signal, the flow switch starts the compressor, which begins to pump air into the container through the tube.
3. The liquid is mixed with gas and thus saturated with oxygen and poured into a reservoir under significant pressure.
4. This mixture is allowed to settle for 30 minutes (or longer) to allow oxidation reactions to occur and sediment to settle, after which it is passed through filters that absorb solid particles and sent to points of consumption.
Or another scheme is possible:
- The working medium is collected in a volumetric container, for example, in a special column.
- At the level of the middle of the tank, oxygen is supplied, which begins to rise.
- Reaching the top, the gas not only naturally starts the aeration process, but also systematically accelerates it.
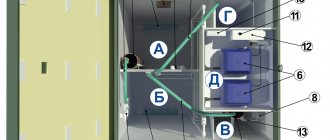
Design of a standard installation for gravity aeration
Aerator
This is a device for supplying air to the system. To perform this procedure, depending on the design features of the device, an ejector, a compressor or a showering system is used.
Contact capacitance
The main part of the gravity aeration device. This is a closed housing where the process of enriching water with oxygen and settling it takes place. At the top of the tank there is a breathing valve through which harmful gases and excess O2 are removed.
Centrifugal pump
Pumps out settled water from the contact tank and supplies it to the system for further use.
Automation
The main element of automation is most often a level control relay. A sensor located in the tank transmits a signal to it about the water level in the tank. If this indicator has reached the maximum permissible limit, the relay sends a command to the solenoid valve to shut off the water supply to the tank, and the pump receives a command to start pumping it out.
What are aeration water purification systems?
Each of them is a set of equipment that differs from analogues and competitors in the degree of complexity, performance, reliability, but necessarily has the following advantages:
- autonomous functioning (or with minimal human intervention;
- ease of maintenance - low maintenance and low investment of time and money to maintain all modules and components in working order;
- compact dimensions - for trouble-free installation not only in production, but also in a personal plot or even in a house;
- economic efficiency.
Advantages and disadvantages of gravity aeration
Advantages of gravity aeration compared to other water treatment methods:
Cleaning is done without chemicals
Environmental Safety
Simplicity and low cost of maintenance
No constant water pressure required
Possibility of using automation systems
Handling large volumes of liquid
The disadvantages include the large dimensions of the equipment and its relatively high cost. But even despite the price of the device, due to the low cost of operation, the overall economic efficiency is higher than most other methods of water purification.
Aeration of water from a well
Yes, it may also contain impurities, and if they were not there yesterday, according to experts, this does not mean that harmful substances will not appear in it tomorrow, after the composition of the soil changes. So it’s better to play it safe and filter it, especially if it is used for food, and for other household purposes too, because otherwise the sewerage pipes or watering seedlings in the greenhouse will sooner or later become clogged due to sediments.
Properly selected equipment will allow you to quickly remove excess manganese and other metals, hydrogen sulfide. It is important to use a filter that can capture even relatively small particles of sediment and will not clog for a long time.
Main table dispenser AquaPro 929CH/RO (cooling/heating)
Floor dispenser AquaPro 311 (empty, without cooling)
Floor-standing dispenser AquaPro 6207CH (cooling/heating/room temp.)
How to deferrize water with your own hands
At home, water can be purified using special filters. Such devices are produced from Tyumen. They have a replaceable cartridge, which consists of a porous active material that can retain various suspensions, including iron salts. They are not recommended for installation on water supply networks that contain residual chlorine, as this leads to rapid failure of their filter element.
In individual water supply systems, gravity purification units with and without a compressor are used. Due to the fact that, in addition to the submersible pump, a pumping station is needed to provide the house with water suitable for consumption, such installations require a lot of space for installation and cannot be used in apartments. When the concentration of metals in the well is low, the ejector aeration method is used.
How and where is simplified water aeration used?
It can be used with any of the approaches if the liquid is capable of creating a catalytic film during the process of enrichment with oxygen and precipitation. This will not happen if the concentration of the same iron is below 70% of all impurities. The current oxygen content is also important: it should be at a level of 6 mg/l. And we should not forget about the height of the spout - 0.5 m above the drop level.
There are factors that reduce the effectiveness of the procedure, or reduce the result to zero, and these are:
- low pH level;
- too strong oxidation;
- presence of carbon dioxide or hydrogen sulfide.
The scheme of the method is as simple as possible: the working medium passes through the nozzles, simultaneously being saturated with air, falling into the tank and immediately draining into the main channel. In this case, there is no storage tank, which significantly reduces costs, but also does not allow for the maximum degree of purification.
How to set up the process of aerating water from a well with your own hands
You can organize an effective system yourself - for this you need:
- install a pump that draws from the source;
- connect to it saturation equipment located in the basement of the house or other suitable warm place with a stable microclimate and humidity level;
- connect to it a filter with a capacity of 250 l/day (it is better to take it with a reserve, for all household needs);
- then place a settling tank of the appropriate capacity;
- connect it all with pipes that should be led to plumbing, heater and other points of consumption.
Or you can do it easier and buy a ready-made system that has proven its reliability in practice. Specialists from the Water of the Fatherland organization can help you make your choice based on your goals and capabilities.
The use of aeration for iron removal and removal of organic matter
One of the following schemes is implemented:
- Pressure - the working medium is pumped and passes through the catalyst, which significantly accelerates the oxidation reactions. The amount and strength of air exposure is regulated by the compressor; impurities are precipitated as the flow passes through a filter with sorption granules, which are then washed into the drainage.
- Non-pressure - a constantly high pressure is no longer maintained in the container, as a result of which water passes through the system somewhat slower than in the previous case, because it requires some time to be enriched with oxygen and settle. After which it is pumped into a deferrizer, partially filled with a substance that causes the transformation of dissolved elements into solid ones.
- Reagents + pressure – using a dispenser, sodium hypochlorite is introduced into the liquid, which immediately reacts due to the pressure. Then the working medium is directed into a tank with filter granules, on which impurities are deposited. Residual suspended matter is washed out with a reverse flow, and excess NaOCl is eliminated by sorption materials.
- Reagents without pressure - the scheme is similar to the previous one, the only difference is that water with a catalyst added to it is first settled in a special tank for about 30-60 minutes - to start and carry out oxidation reactions - and only then goes further through the system.
It’s the last two methods that also help remove organic matter.
Methods for purifying water from iron using a filter and aerator
The choice of the type of water deferrization plant with aeration depends on the type of metals contained. Iron may be present in tap water in the following forms:
- Fe(II) - dissolved divalent. It does not change the color of the liquid and is not visually noticeable.
- Fe(III) is insoluble trivalent. Forms a precipitate and gives a “rusty” color.
- Colloidal - tiny solid particles that create turbidity in water.
- Organic - part of organic pollutants.
- Bacterial - forms an iridescent film on the surface of the liquid, as well as a silty sediment at the bottom.
Ferric iron is the easiest to remove. It precipitates and is easily filtered. The remaining forms of iron must first be converted to the filterable form Fe(III). In this case, aeration is used to remove iron from the water. Manganese is found in raw water from underground sources in the form of Mn(II). Its concentration in untreated water can reach 0.1%. The divalent form of the element is partially dissolved and can form a precipitate when the liquid is heated very strongly. To purify water from manganese, it is converted into a trivalent or tetravalent form - it is converted into insoluble compounds (metal oxides, hydroxides, acid salts). This also produces a precipitate that can be caught by filtration.
Iron removal filters
Filtration plants for removing iron and manganese from water are divided into industrial and domestic. They differ in the degree of purification, productivity, type of action, cost, and complexity of maintenance.
By design, there are three categories of iron removal plants:
- Reagent filters . Here, the purified water passes through a granular filler that has a high sorption capacity. In this case, dissolved metal salts are converted into an insoluble form, which settles on the filter granules. To catalyze the process, potassium permanganate, chlorine dioxide, and sodium hypochlorite are used.
- Reagent-free filters . The housing of such a filter is filled with an active catalytic absorber. Previously, when passing through the aerator, oxidation of divalent iron to trivalent iron occurs, followed by precipitation of solid rust particles directly on the deferrization filter. Insoluble flakes settle on the sorbent and are washed off with a stream of water when washing the filter. For an iron removal plant to operate in this manner, aeration is required.
- Filters for complex water purification from iron and hardness . These are complex installations that include several stages of cleaning. They remove iron, manganese, ammonium, and harmful organic compounds from water. They also soften and clarify water. Multifunctional units are compact, economical, and have a simple regeneration system.
Reagent deferrization is used to purify water with low pH and high concentrations of iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide. To regenerate the filter material, backwash the filler with a special solution; the restoration process takes approximately 1.5 hours.
Reagent-free aeration units have a long service life, and their regeneration does not require the consumption of reagents. These filters trap iron, manganese, and dissolved corrosive gases. These are highly efficient units widely used in various industries.
Deferrization of water by aeration
Aeration of water to remove iron is a process of intensive saturation of water with oxygen, as a result of which the iron contained in it is oxidized to an insoluble form. According to the method of aerating water from iron, installations are:
- Pressure . Air is forced by a high-pressure air compressor into the water stream at the inlet of the aeration column or pipe. Excess air is discharged into a separator or air vent, and oxygen-enriched water enters the filter column with catalytic media. Here the final oxidation of iron occurs, as well as the precipitation of undissolved metal and suspended particles. Pressure aerators for iron removal are used even with high water flow rates and high iron content.
- Non-pressure . Such aeration and water deferrization stations operate at low environmental pressures. Because of this, gravity aeration with iron removal is usually used for low water flow rates and low iron concentrations. The liquid is supplied by a water pump through spray nozzles into a special open container. The interaction of iron and oxygen is ensured by the ejection and suffocation of water. Excess air is released through the air valve, and oxidized insoluble iron is deposited in the filter media of the installation.
- Electrochemical oxidation of iron by aeration . Aeration occurs through the use of an electrochemical reaction that converts different types of energy. These are modern, productive installations for water deferrization by aeration, characterized by small dimensions, low noise levels and ease of operation. Suitable for purifying water with high iron content.