The main areas of application of steel 12Х18Н10Т
12Х18Н10Т
is used for the production of parts that operate at temperatures up to +600˚С. Steel is used in the manufacture of products that can be used in conditions of dilute acids, moderately aggressive alkaline and saline solutions - for example, tanks and welded units. This is facilitated by the characteristics of 12x18n10t.
Marking of steel 12Х18Н10Т
12x18n10t decoding
: "12" - 0.12% carbon, "X18" - 18% chromium, "H10" - nickel - 10%, "T" - titanium. The absence of a number for titanium means its content does not exceed 1.0%−1.5%.
Chemical composition in % of steel 12Х18Н10Т
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Mo | Ni | V | Ti | Cu | W | Fe |
| <0,12 | <0,8 | <2,0 | <0,035 | <0,02 | 17,0-19,0 | <0,5 | 9,0-11,0 | <0,2 | <0,8 | <0,4 | <0,2 | Rest |
The chemical composition of 12Х18Н10Т is regulated by GOST 5632-72
:
- Quite a large percentage of chromium (17%–19%).
- Nickel alloying additive (9%–11%).
- Carbon in the alloy is a small concentration (0.1%).
- The alloying element is titanium.
- Silicon (0.8%).
Influence of chemical composition on the properties of steel 12Х18Н10Т
The main additives of complex alloy steel significantly affect its properties:
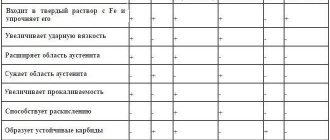
- Chrome improves anti-corrosion qualities.
- Thanks to the introduction of nickel, the steel is included in the category of austenites, and combines all the technological and operational properties of stainless steels.
- The introduction of aluminum, titanium and silicon into the alloy gives 12Х18Н10Т the quality of ferritic steel.
- Titanium creates a carbide-forming effect and prevents the risk of intergranular corrosion.
- Manganese allows the production of steel with a fine-grained structure.
- Silicon increases density and improves fluidity. At the same time, it reduces the level of ductility, which makes cold rolling more difficult.
- The phosphorus content should not exceed 0.035%, as it provokes a decrease in mechanical properties, which complicates the use of steel in the cryogenic area.
12Х18Н10Т - interpretation of steel
The marking 12Х18Н10Т indicates the estimated amount of the main components included in the alloy: 12 - means 0.12% carbon, X18 - percentage composition of chromium, H10 - nickel and T - the presence of titanium. Based on this, it can be determined that the composition of the main chemical elements of stainless steel grade 12Х18Н10Т includes:
- about 67% iron;
- up to 0.12% carbon;
- 17-19% chromium;
- 9-11% nickel;
- up to 2% magnesium;
- up to 1% titanium;
- up to 0.8% silicon.
In addition, the chemical composition of the metal contains in small quantities: sulfur, copper, silicon, manganese and phosphorus.
The high anti-corrosion properties of steel 12Х18Н10Т are ensured by the high chromium content. The presence of nickel promotes the austenitic structure of the metal and allows, as a result, to combine the expansion of the operational characteristics of steel with excellent manufacturability during processing. In addition, the presence of nickel in the alloy changes its properties and increases the metal’s resistance to acids and alkalis.
The presence of titanium and silicon in steel leads to the formation of ferrite, which changes the characteristics, eliminates intergranular corrosion in welds, slows down the rate of grain growth when heated and increases the density of the resulting ingot.
Mechanical properties of stainless steel 12Х18Н10Т
Heat treatment modes include the use of hardening as a result of heating to 1100ºC with subsequent cooling in water. Stainless steel sections up to 35 mm can be cooled in the open air. Temperature limits for forging are from 850ºC to 1200ºC.
The specific gravity of the metal is 7920 kg/m3. The hardness of steel HB 10-1 = 179 MPa, with an endurance limit of 279 MPa.
The technology of welded joints does not have any special restrictive properties. The following characteristics of welding technologies are used:
- manual electric arc, using TsT-26 electrodes;
- electroslag;
- contact point.
To ensure increased strength, final heat treatment of the seams is recommended.
Mechanical properties of material 12Х18Н10Т
Mechanical properties of steel at elevated temperatures
| Test temperature, °C | Yield strength, σ0.2, MPa | Tensile strength, σв, MPa | Elongation at break, δ5, % | Relative narrowing, ψ, % | Impact strength KCU at 20°C, J/cm2 |
| 20 | 225 — 315 | 550 — 650 | 46 — 74 | 66 — 80 | 215 — 372 |
| 500 | 135 — 205 | 390 — 440 | 30 — 42 | 60 — 70 | 196 — 353 |
| 550 | 135 — 205 | 380 — 450 | 31 — 41 | 61 — 68 | 215 — 353 |
| 600 | 120 — 205 | 340 — 410 | 28 — 38 | 51 — 74 | 196 — 358 |
| 650 | 120 — 195 | 270 — 390 | 27 — 37 | 52 — 73 | 245 — 353 |
| 700 | 120 — 195 | 265 — 360 | 20 — 38 | 40 — 70 | 255 — 353 |
Impact strength of steel, KCU, J/cm2
| Heat treatment | Т= +20 °С | Т= -40 °С | Т= -75 °С |
| Strip 8x40 mm at rest | 286 | 303 | 319 |
Sensitivity of steel to aging embrittlement
| Time watch | Temperature, °C | Impact strength, KCU, J/cm2 |
| The initial state | — | 274 |
| 5000 | 600 | 186 — 206 |
| 5000 | 650 | 176 — 196 |
Heat resistance of steel
| Wednesday | Temperature, ºС | Strength group or score |
| Air | 650 | 2 — 3 |
| Air | 750 | 4 — 5 |
Main characteristics of steel 12Х18Н10Т
12Х18Н10Т
is a high-carbon, corrosion-resistant, non-magnetic, titanium-containing steel.
Austenite group. Refers to complex alloys. Due to the presence of chromium and nickel in the alloy, this steel is also called stabilized chromium-nickel steel. Today it is the most used and widespread steel of all stainless steel grades. The main advantages of steel 12Х18Н10Т
are high strength, hardness, impact strength and ductility.
Characterized by excellent weldability and hygiene. Among the advantages are heat resistance and heat resistance, cryogenic qualities - the temperature limits for operation (without loss of properties) are enormous, from -196˚С to +600˚С
.
Stainless steel 12Х18Н10Т
Substitutes
Substitute - steels 08Х18Г8Н2Т, 10Х14Г14Н4Т, 12Х17Г9А4, 08Х22Н6Т, 08Х17Т, 15Х25Т, 12Х18Н9Т.
Foreign analogues
| Germany DIN | Brand | X10CrNiTi18-9 |
| Number | 1.4541 | |
| USA (AISI, SAE, ASTM) | 321 | |
| France (AFNOR) | Z10CN18 | |
| UK (BS) | 320S31 | |
| Sweden (SS) | 2337 | |
| Italy UNI | — | |
| Japan | SUS321 | |
IMPORTANT!!! The possibility of replacement is determined in each specific case after assessing and comparing the properties of steels
Interpretation of steel 12Х18Н10Т
The number 12 indicates the average carbon content in hundredths of a percent, i.e. for steel 12Х18Н10Т this value is 0.12%.
The letter “X” indicates the chromium content of the steel. The number 18 after the letter “X” indicates the approximate amount of chromium in steel as a percentage, rounded to the nearest whole number, i.e. chromium content about 18%.
The letter “N” indicates the nickel content of the steel. The number 10 after the letter “N” indicates the approximate amount of nickel in steel as a percentage, rounded to the nearest whole number, i.e. Nickel content is about 10%.
The letter "T" indicates the titanium content of the steel. The titanium content in steel does not exceed 1.5%.
Type of delivery
Long products, including shaped steel: GOST 5949-75, GOST 2590-88, GOST 2879-88. Calibrated rod GOST 7417-75, GOST 8559-75, GOST 8560-78. Polished rod and silver steel GOST 14955-77, GOST 18907-73. Thick sheet GOST 7350-77. Thin sheet GOST 5582-75. Tape GOST 4986-79. Wire GOST 18143-72. Forgings and forged blanks GOST 25054-81, GOST 1133-71. Pipes GOST 9940-72, GOST 9941-72, GOST 14162-79.
Weldability
Steel 12Х18Н10Т is weldable without restrictions. Welding methods: RDS, ESW and KTS (Contact Spot Welding). Subsequent heat treatment is recommended.
Technological properties
Forging temperature, °C: beginning 1200, end 850. Sections up to 350 mm are cooled in air. Cutting machinability - Kv tv.spl = 0.85 and Kv b.st = 0.35 in the hardened state at HB 169 and σw = 610 MPa. Flock sensitivity - not sensitive.
Chemical composition, % (GOST 5632-2014)
| Steel | C | Si | Mn | Cr | Ni | Ti | S | P |
| 12Х18Н10Т | no more than 0.12 | no more than 0.80 | no more than 2.00 | 17,0-19,0 | 9,0-11,0 | 5,0-8,0 | no more than 0.02 | no more than 0.40 |
Application of 12Х18Н10Т
Purpose - parts operating up to 600 °C; welded machines and vessels operating in dilute solutions of nitric, acetic, phosphoric acids, solutions of alkalis and salts and other parts operating under pressure at temperatures from -196 to +600 °C, and in the presence of aggressive media - up to +350 °C.
Corrosion-resistant (stainless) steel is of the austenitic class and is mainly used as corrosion-resistant, but can also be used as heat-resistant and heat-resistant. In terms of heat resistance, it is close to steel 12Х18Н9Т.
It is used for the manufacture of welded equipment in various industries.
Approximate application as heat-resistant steel
Purpose: pipes, furnace fittings, heat exchangers, muffles, retorts, exhaust pipes and manifolds, spark plug electrodes. Recommended maximum temperature for long-term use (up to 10,000 hours), 800°C.
The temperature at which intense scale formation begins in air is 850°C.
Unstable in sulfur-containing environments. They are used in cases where nickel-free steels cannot be used.
Approximate application as heat-resistant steel
Exhaust system parts, pipes, sheet and section parts.
Recommended maximum application temperature is 600°C.
Service life - Very long.
The temperature at which intense scale formation begins in air is 850°C.
Application of steel 12Х18Н10Т for bodies, covers, flanges, membranes and valve assembly made from rolled products, forgings (stampings) (GOST 33260-2015)
| steel grade | ND for supply | Temperature of the working medium (wall), °C | Additional instructions for use |
| 12Х18Н10Т GOST 5632 | Long products GOST 5949. Sheets GOST 7350. Forgings GOST 25054. Pipes GOST 9940, GOST 9941 (made of 12Х18Н10Т) | -270 to 350 | For welded fittings operating in aggressive environments: HNO3, alkalis, ammonium nitrate, food media, special equipment media, ship fittings, cryogenic media, hydrogen sulfide-containing media; for membranes |
| St. 350 to 610 | For welded reinforcement assemblies in the absence of a requirement for resistance to intergranular corrosion |
Application of steel 12Х18Н10Т for fittings fasteners (GOST 33260-2015)
| Steel grade, according to GOST 1759.0 | Material standard or specification | Application options | |||||
| Bolts, studs, screws | Nuts | Flat washers | |||||
| Ambient temperature, °C | Nominal pressure Pn, MPa (kgf/cm2) | Ambient temperature, °C | Nominal pressure Pn, MPa (kgf/cm2) | Ambient temperature, °C | Nominal pressure Pn, MPa (kgf/cm2) | ||
| 12Х18Н10Т | GOST 5632 | -196 to 600 | Not regulated | -196 to 600 | Not regulated | -196 to 600 | Not regulated |
The use of steel 12Х18Н10Т for the manufacture of spindles and rods (GOST 33260-2015)
| steel grade | ND for supply | Working environment temperature, °C | Additional instructions for use |
| 12Х18Н10Т GOST 5632 | Long products GOST 5949 | -270 to 350 | It is used for work in aggressive environments: nitric acid, alkalis, ammonium nitrate, food environments, environments of special equipment, shipbuilding, cryogenic equipment and hydrogen sulfide-containing environments. Used for welded joints |
| Long products GOST 5949 | St. 350 to 610 | Suitable for use in environments that do not cause intergranular corrosion |
Application of steel 12Х18Н10Т for bellows (GOST 33260-2015)
| steel grade | ND for supply | RD for the production of bellows | Working environment temperature, °C | Operating pressure Pp, MPa (kgf/cm2), no more | Additional instructions for use |
| 12Х18Н10Т GOST 5632 | Sheet GOST 5582. Tape GOST 4986, (for steel 1.4541) | GOST 21744, GOST 22388 | -260 to 550 | From 0.6 to 25.0 (from 6 to 250) | For water, steam, inert gases and cryogenic temperatures. For mildly aggressive environments - up to a temperature of 350°C. For corrosive environments - up to 150°C |
| Pipe GOST 10498 | -260 to 465 | From 0.15 to 3.10 (from 1.5 to 31.0) |
NOTE The table shows the limit values for temperatures and operating pressures. Specific combinations of application parameters (working pressure, axial stroke, temperature and full assigned life) are given in the regulatory documentation for bellows.
Application of steel 12Х18Н10Т for valve valve assembly
| steel grade | Working environment temperature, °C | Hardness | Additional instructions for use |
| 12Х18Н10Т GOST 5632 | -100 to 300 | 155…170 HB | The functionality of the valve assembly is ensured by the presence of surfacing or other wear-resistant coating in the mating part |
Application of steel 12Х18Н10Т for helical coil springs
| steel grade | ND for supply | Application temperature, °C | Additional instructions for use |
| 12Х18Н10Т GOST 5632 | Wire | -253 to 400 | Safety, control valves, low-magnetic springs |
Application of steel 12Х18Н10Т for gaskets
| steel grade | Type of semi-finished product | Application temperature, °C | Additional instructions for use | |
| Name | ND for supply | |||
| 12Х18Н10Т GOST 5632 | Thick heat-treated sheets | GOST 7350 | -253 to 600 | Suitable for use in corrosive environments |
Resistance of steel 12Х18Н10Т to sulfide corrosion cracking
| Method of forming blanks | Name of parts |
| Forgings, stampings, rolled products | Body, bonnet, stem, spindle, valve seal parts, bellows end parts |
Maximum permissible temperature for the use of steel 12Х18Н10Т in environments containing ammonia
| steel grade | Temperature of application of steels, °C at partial pressure of ammonia, MPa (kgf/cm) | ||
| St. 1(10) to 2(20) | St. 2(20) to 5(50) | St. 5(50) to 8(80) | |
| 12Х18Н10Т | 540 | 540 | 540 |
Maximum permissible temperature for the use of steel 12Х18Н10Т in hydrogen-containing environments
| steel grade | Temperature, °C, at partial pressure of hydrogen, PH2, MPa (kgf/cm2) | ||||||
| 1,5(15) | 2,5(25) | 5(50) | 10(100) | 20(200) | 30(300) | 40(400) | |
| 12Х18Н10Т | 510 | 510 | 510 | 510 | 510 | 510 | 510 |
NOTE
- The parameters for using steels indicated in the table also apply to welded joints.
- The partial pressure of hydrogen is calculated by the formula: PH2 = (C*Pp)/100, where C is the percentage in the system; PH2—hydrogen partial pressure; Pp is the operating pressure in the system.
Relative erosion resistance coefficient of reinforcement parts made of steel 12Х18Н10Т
| Details of the flow part of the fittings | Part material | Erosion resistance coefficient relative to steel 12X18H10T | Maximum pressure drop at which there is no erosive wear, MPa |
| Body, pipes, rod, plunger (gate), seat | 12Х18Н10Т | 1,0 | 4,0 |
NOTE
- The coefficient of erosion resistance of a material is the ratio of the rate of erosive wear of the material to the rate of erosive wear of steel 12Х18Н10Т (taken as 1).
- Materials are erosion-resistant if the coefficient of relative erosion resistance Kn is at least 0.5 and the hardness of the material is HRC≥28.
Resistance of steel 12Х18Н10Т against crevice erosion
| Durability group | Point | Erosion resistance against steel 12X18H10T |
| Persistent | 2 | 0,75-1,5 |
Resistance of steel 12Х18Н10Т against impact erosion
| Toughness Point | NV no more | Materials |
| 5 | 150 | Austenitic chromium-nickel stainless steel grade 12Х18Н10Т |
Application of steel 12Х18Н10Т for the manufacture of main parts of nuclear power plant fittings
| steel grade | Type of semi-finished product or product | Maximum permissible temperature of use, °C |
| 12Х18Н10Т GOST 5632, GOST 24030 | Sheets, pipes, forgings, long products. Fasteners | 600 |
Characteristics
Density ρ at test temperature, 20 °C - 7900 kg/cm3
Thermal conductivity coefficient λ W/(m*K) at test temperature, °C
| Steel | 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 900 |
| 12Х18Н10Т | 15 | 16 | 18 | 19 | 21 | 23 | 25 | 27 | 26 | — |
Electrical resistivity ρ, nOhm*m, at test temperature °C —
| Steel | 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 900 |
| 12Х18Н10Т | 725 | 792 | 861 | 920 | 976 | 1028 | 1075 | 1115 | — | — |
Specific heat capacity c, J/(kg*K), at test temperature, °C
| 20-100 | 20-200 | 20-300 | 20-400 | 20-500 | 20-600 | 20-700 | 20-800 | 20-900 | 20-1000 |
| 462 | 496 | 517 | 538 | 550 | 563 | 575 | 596 | — | — |
Thermal conductivity coefficient λ, W/(m*K), at test temperature, °C
| 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 900 |
| 15 | 16 | 18 | 19 | 21 | 23 | 25 | 27 | 26 | — |
Linear expansion coefficient α*106, K-1, at test temperature, °C
| 20-100 | 20-200 | 20-300 | 20-400 | 20-500 | 20-600 | 20-700 | 20-800 | 20-900 | 20-1000 |
| 16,6 | 17,0 | 17,2 | 17,5 | 17,9 | 18,2 | 18,6 | 18,9 | 19,3 |
Modulus of normal elasticity E, GPa, at test temperature °C
| Steel | 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 900 |
| 12Х18Н10Т | 198 | 194 | 189 | 181 | 174 | 166 | 157 | 147 | — | — |
Modulus of elasticity in torsional shear G, GPa, at test temperature °C
| Steel | 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 900 |
| 12Х18Н10Т | 77 | 74 | 71 | 67 | 63 | 59 | 57 | 54 | 49 | — |
Mechanical properties
| GOST | Delivery status | Section, mm | σ0.2, MPa | σb, MPa | δ5, % | ψ% |
| no less | ||||||
| GOST 5949-75 | Bar. Quenching from 1020-1100 °C in air, oil or water | 60 | 196 | 510 | 40 | 55 |
| GOST 18907-73 | Ground rod, processed to a specified strength | — | — | 590-830 | 20 | — |
| Cold-worked rod | Up to 5 | — | 930 | — | — | |
| GOST 7350-77 (transverse samples) | Hot-rolled and cold-rolled sheets: | |||||
| hardening from 1000-1080 °C in water or air | St.4 | 236 | 530 | 38 | — | |
| GOST 5582-75 (transverse samples) | hardening from 1050-1080 °C in water or air | Up to 3.9 | 205 | 530 | 40 | — |
| hard-worked | Up to 3.9 | — | 880-1080 | 10 | — | |
| GOST 25054-81 | Forging. Quenching from 1050–1100 °C in water or air | Up to 1000 | 196 | 510 | 35 | 40 |
| GOST 18143-72 | Heat treated wire | 1,0-6,0 | — | 540-880 | 20 | — |
| GOST 9940-81 | Seamless hot-deformed pipe without heat treatment | 3,5-32 | — | 529 | 40 | — |
Mechanical properties at elevated temperatures
| tsp, °С | σ0.2, MPa | σa, MPa | δ5, % | ψ% | KCU, J/cm2 |
| 20 | 225-315 | 550-650 | 46-74 | 66-80 | 215-372 |
| 500 | 135-205 | 390-440 | 30-42 | 60-70 | 196-353 |
| 550 | 135-205 | 380-450 | 31-41 | 61-68 | 215-353 |
| 600 | 120-205 | 340-410 | 28-38 | 51-74 | 196-358 |
| 650 | 120-195 | 270-390 | 27-37 | 52-73 | 245-353 |
| 700 | 120-195 | 265-360 | 20-38 | 40-70 | 255-353 |
Note.
Hardening from 1050-1100 °C in air.
Mechanical properties during long-term strength testing (GOST 5949-75)
| tsp, °С | Creep limit, MPa, not less | Creep rate, %/h |
| 600 | 74 | 1/100000 |
| 650 | 29-39 |
| tsp, °С | Long-term strength limit, MPa, not less | τ, h |
| 600 | 147 | 10000 |
| 650 | 78-98 |
Impact strength KCU
| Delivery status | KCU, J/cm2, at temperature, °C | ||
| +20 | -40 | -75 | |
| Strip 8×40 mm | 286 | 303 | 319 |
Note.
Fatigue limit σ-1 = 279 MPa at n = 107.
Sensitivity to aging embrittlement
| Time, h | Temperature, °C | KCU, J/cm2 |
| Ref. comp. | Ref. comp. | 274 |
| 5000 | 600 | 186-206 |
| 5000 | 650 | 176-196 |
Heat resistance
| Wednesday | Temperature, °C | Strength group or score |
| Air | 650 | 2-3 |
| 750 | 4-5 |
Find out more
Low-alloy structural steel for welding…
Structural alloy steel 20ХН3А…
Steel St2kp - carbon steel of ordinary quality...
Stainless steel 08Х18Н10Т
Physical properties
| Temperature, °C | Modulus of elasticity, E 105, MPa | Linear expansion coefficient, a 10 6, 1/°С | Thermal conductivity coefficient, l, W/m °C | Specific heat capacity, C, J/kg °C | Electrical resistivity, R 10 9, Ohm m |
| 20 | 1,98 | — | 15 | — | 725 |
| 100 | 1,94 | 16,6 | 16 | 462 | 792 |
| 200 | 1,89 | 17,0 | 18 | 496 | 861 |
| 300 | 1,81 | 17,2 | 19 | 517 | 920 |
| 400 | 1,74 | 17,5 | 21 | 538 | 976 |
| 500 | 1,66 | 17,9 | 23 | 550 | 1028 |
| 600 | 1,57 | 18,2 | 25 | 563 | 1075 |
| 700 | 1,47 | 18,6 | 27 | 575 | 1115 |
| 800 | — | 18,9 | 26 | 596 | — |
| 900 | — | 19,3 | — | — | — |
Technological properties
| Specific gravity | 7920 kg/m3 |
| Heat treatment | Quenching 1050 - 1100oC, water |
| Forging temperature | Start 1200°C, end 850°C. Sections up to 350 mm are cooled in air |
| Material hardness | HB 10 -1 = 179 MPa |
| Weldability of the material | Without restrictions, welding methods: RDS (electrodes TsT-26), EShS and KTS. Subsequent heat treatment is recommended |
| Machinability | In the hardened state at HB 169 and σв = 610 MPa, Ku tv. spl=0.85, Ku b. st=0.35 |
| Flock sensitivity | Not sensitive |
| Heat resistance | In air at T=650 °C 2-3 resistance group, at T=750 °C 4-5 resistance group |
| Endurance limit | σ-1=279 MPa, n=107 |
Technological abilities and processing of steel 12Х18Н10Т
Properties such as weldability, ductility and impact strength are significantly increased by quenching in ordinary water, but the hardness is reduced. So the optimal heat treatment is hardening at 1050°C–1080°C.
Steel 12Х18Н10Т
welds perfectly and has no restrictions. And to increase the strength and reliability of the seams, heat treatment is necessary, since the area of the seams must also be resistant to intergranular type corrosion.
Material delivery forms
| Metal forming. Forgings | GOST 25054-81; |
| Long and shaped rolled products | GOST 2879-2006; GOST 1133-71; GOST 2591-2006; GOST 2590-2006; |
| Sheets and strips | GOST 103-2006; GOST 19904-90; GOST 19903-74; |
| Long and shaped rolled products | GOST 18907-73; GOST 8560-78; GOST 8559-75; GOST 7417-75; GOST 5949-75; |
| Sheets and strips | GOST 10885-85; GOST 51393-99; GOST 7350-77; GOST 5582-75; GOST 4405-75; |
| Ribbons | GOST 4986-79; |
| Steel pipes and connecting parts for them | GOST 11068-81; GOST 19277-73; GOST 14162-79; GOST 9941-81; GOST 9940-81; |
| Alloy steel wire | GOST 18143-72; |
| Metal mesh | GOST 3187-76; GOST 3306-88; GOST 9074-85. |
Application of steel 12Х18Н10Т taking into account characteristics and properties
Steel grade 12Х18Н10Т
has a very diverse scope of application, which, first of all, is shown by the decoding of steel 12x18n10t. Due to its resistance to aggressive media (except for sulfur-containing media), it is in demand in the chemical industry - in the production of vessels operating under high pressure.
Made from steel 12Х18Н10Т
pipelines for transporting dilute solutions of phosphoric, nitric, acetic acids, aggressive bases and salts, pipes for connecting equipment with increased radiation.
Seamless stainless steel pipes 12Х18Н10Т
are indispensable in all areas of the food industry, oil and oil refining, chemical and fuel and energy industries. It is actively used in the automotive, shipbuilding, aviation and industrial fields.
In addition, 12Х18Н10Т
used in cryogenic technology at extremely low temperatures - down to -269˚С, which does not interfere with its use at high temperatures (as in arc furnaces).
Sheets 12Х18Н10Т
used as construction and finishing metal.
No less popular are pipes made of 12Х18Н10Т
, forgings of parts for mechanical engineering, wire, circle, tape, etc. Wire is used for welding work. In the form of threads or cords, steel is suitable for the manufacture of meshes, springs, cables and ropes.
The closest equivalents (analogues) of steel 12Х18Н10Т
| USA (ASTM/AISI) | 321, 321H, S32100, S32109 |
| Germany (DIN, WNr) | 1.4541, 1.5878, X10CrNiTi18-10, X12CrNiTi18-9, X6CrNiTi18-10 |
| Japan (JIS) | SUS321 |
| France (AFNOR) | Z10CN18-10, Z10CN18-11, Z6CN18-10, Z6CNT18-12 |
| England (BS) | 321S31, 321S51, 321S59, LW18, LW24, X6CrNiTi18-10 |
| Euronorms (EN) | 1.4541, 1.4878, X10CrNiTi18-10, X6CrNiTi18-10KT |
| Italy (UNI) | X6CrNiTI18-11, X6CrNiTi18-11KG, X6CrNiTi18-10KT |
| Spain (UNE) | F.3523, X6CrNiTi18-10 |
| China (GB) | 0Cr19Ni10Ti, 0Cr18Ni11Ti, 0Cr18Ni9Ti, 1Cr18Ni11Ti, H0Cr20Ni10Ti |
| Sweden (SS) | 2337 |
| Bulgaria (BDS) | 0Ch148N10T, Ch18N12T, Ch18N9T, X6CrNiTi18-10 |
| Hungary (MSZ) | H5Ti, KO36Ti, KO37Ti, X6CrNi18-10 |
| Poland (PN) | 0H18N10T, 1H18N10T, 1H18N12T, 1H18N9T |
| Romania (STAS) | 10TiNiCr180, 12TiNiCr180 |
| Czech Republic (CSN) | 17246, 17247, 17248 |
| Austria (ONORM) | X6CrNiTi18-10KKW, X6CrNiTi18-10S |
| Australia (AS) | 321 |
| South Korea (KS) | STS321, STS321TKA, STSF321 |
| Russia (GOST) | 10Х14Г14Н4Т, Х14Г14Н3Т |
Foreign analogues
Among the steels produced in other countries of the world that are similar in chemical composition and characteristics, it should be noted:
- 321, 321H, S32100 in the USA;
- SUS321 steel in Japan;
- 0Cr18NiTi18-11, 0Cr18Ni11Ti, 1Cr18Ni11Ti in China;
- STS321 in South Korea;
- 2337 in Sweden;
- 1.4541, 1.4878, X10CrNiTi18-10 in the European Union.
It should be noted that in addition to the pan-European standards to which steel 12Х18Н10Т corresponds, each EU state has its own marking for this alloy. So, for example, in Germany it is X12CrNiTi18-9, in the UK it is steel grades 321S31, 321S51 and LW18. A single European standard for stainless metals has not yet been developed.
Cost of rolled steel and forgings from steel 12Х18Н10Т
The price of materials made from stainless steel 12Х18Н10Т is determined by:
- complexity of the rolled section;
- the quality and properties that steel has;
- degree of surface treatment;
- warehouse and transportation costs;
- existing offers on the market.
In addition, the cost of the order may be influenced by its volume and the method of purchasing materials.
Very often, stainless steel 12Х18Н10Т is sold at dumping prices, which is usually explained by the low quality of the material. For example, sheet steel of this grade is sold at a price of 230-330 rubles/kg, and the maximum price for second-grade metal does not exceed 180 rubles/kg.
Rental release is carried out by weight. In this case, the quality of surface treatment and technical characteristics have a great influence. The average cost of matte sheets with a thickness of 1.0 mm is 260 rubles / kg, and a polished sheet costs two to three times more.
Another factor in determining the price of 12Х18Н10Т depends on the location of the buyer. In the central regions of the country, the cost is lower than in remote regions. This is explained by the small number of competitive offers on the rolled metal market, as well as an increase in transportation costs.
Placing an order, purchasing and delivery in companies
The companies offer all interested organizations, enterprises and individuals to buy stainless rolled steel grade 12Х18Н10Т at the best prices on the rolled metal market. To receive technical advice, clarify prices, characteristics and fill out an application, you need to call the companies. It is also possible to simply leave a request on the website and a specialist will contact you as soon as possible.
The presence of stainless steel 12Х18Н10Т in the warehouse allows us to ensure the fastest delivery of metal to the address specified in the application. If desired, the client can always ensure that the goods are received on a self-pickup basis.
Companies are always ready to discuss the issue of providing discounts to regular and wholesale customers. Working with us is always profitable and convenient.
Rate this article:
Rating: 5/5 — 1 votes